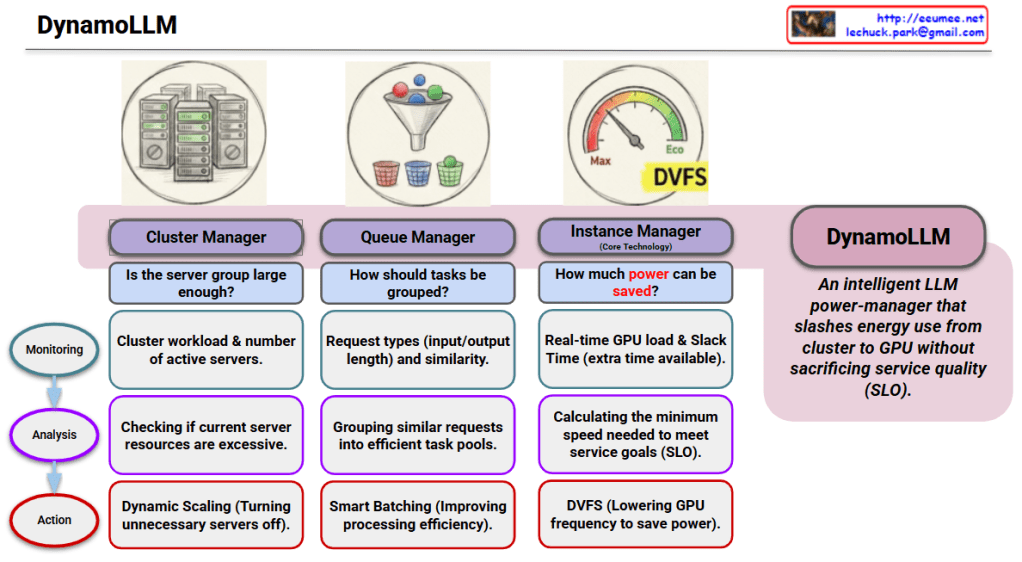
The provided infographic illustrates DynamoLLM, an intelligent power-saving framework specifically designed for operating Large Language Models (LLMs). Its primary mission is to minimize energy consumption across the entire infrastructure—from the global cluster down to individual GPU nodes—while strictly maintaining Service Level Objectives (SLO).
## 3-Step Intelligent Power Saving
1. Cluster Manager (Infrastructure Level)
This stage ensures that the overall server resources match the actual demand to prevent idle waste.
- Monitoring: Tracks the total cluster workload and the number of currently active servers.
- Analysis: Evaluates if the current server group is too large or if resources are excessive.
- Action: Executes Dynamic Scaling by turning off unnecessary servers to save power at the fleet level.
2. Queue Manager (Workload Level)
This stage organizes incoming requests to maximize the efficiency of the processing phase.
- Monitoring: Identifies request types (input/output token lengths) and their similarities.
- Analysis: Groups similar requests into efficient “task pools” to streamline computation.
- Action: Implements Smart Batching to improve processing efficiency and reduce operational overhead.
3. Instance Manager (GPU Level)
As the core technology, this stage manages real-time power at the hardware level.
- Monitoring: Observes real-time GPU load and Slack Time (the extra time available before a deadline).
- Analysis: Calculates the minimum processing speed required to meet the service goals (SLO) without over-performing.
- Action: Utilizes DVFS (Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling) to lower GPU frequency and minimize power draw.
# Summary
- DynamoLLM is an intelligent framework that minimizes LLM energy use across three layers: Cluster, Queue, and Instance.
- It maintains strict service quality (SLO) by calculating the exact performance needed to meet deadlines without wasting power.
- The system uses advanced techniques like Dynamic Scaling and DVFS to ensure GPUs only consume as much energy as a task truly requires.
#DynamoLLM #GreenAI #LLMOps #EnergyEfficiency #GPUOptimization #SustainableAI #CloudComputing
With Gemini