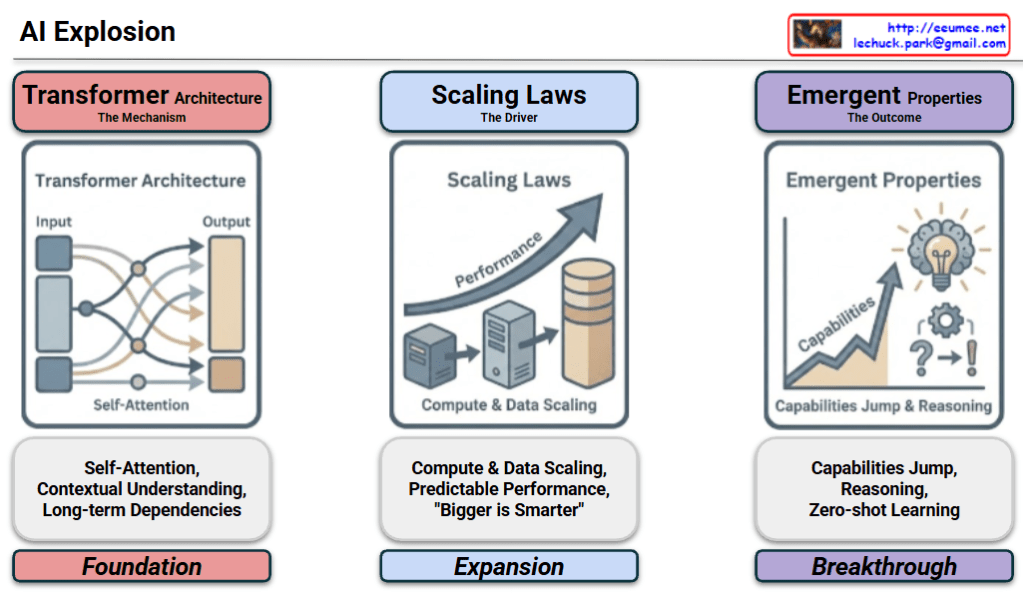
Analysis of the “AI Explosion” Diagram
This diagram provides a structured visual narrative of how modern AI (LLM) achieved its rapid advancement, organized into a logical flow: Foundation → Expansion → Breakthrough.
1. The Foundation: Transformer Architecture
- Role: The Mechanism
- Analysis: This is the starting point of the explosion. Unlike previous sequential processing models, the “Self-Attention” mechanism allows the AI to grasp context and understand long-term dependencies within data.
- Significance: It established the technical “container” capable of deeply understanding human language.
2. The Expansion: Scaling Laws
- Role: The Driver
- Analysis: This phase represents the massive injection of resources into the established foundation. It follows the principle that performance improves predictably as data and compute power increase.
- Significance: Driven by the belief that “Bigger is Smarter,” this is the era of quantitative growth where model size and infrastructure were aggressively scaled.
3. The Breakthrough: Emergent Properties
- Role: The Outcome
- Analysis: This is where quantitative expansion leads to a qualitative shift. Once the model size crossed a certain threshold, sophisticated capabilities that were not explicitly taught—such as Reasoning and Zero-shot Learning—suddenly appeared.
- Significance: This marks the “singularity” moment where the system moves beyond simple pattern matching to exhibiting genuine intelligent behaviors.
Summary
The diagram effectively illustrates the causal relationship of AI evolution: The Transformer provided the capability to learn, Scaling Laws amplified that capability through size, and Emergent Properties were the revolutionary outcome of that scale.
#AIExplosion #LLM #TransformerArchitecture #ScalingLaws #EmergentProperties #GenerativeAI #TechTrends
With Gemini