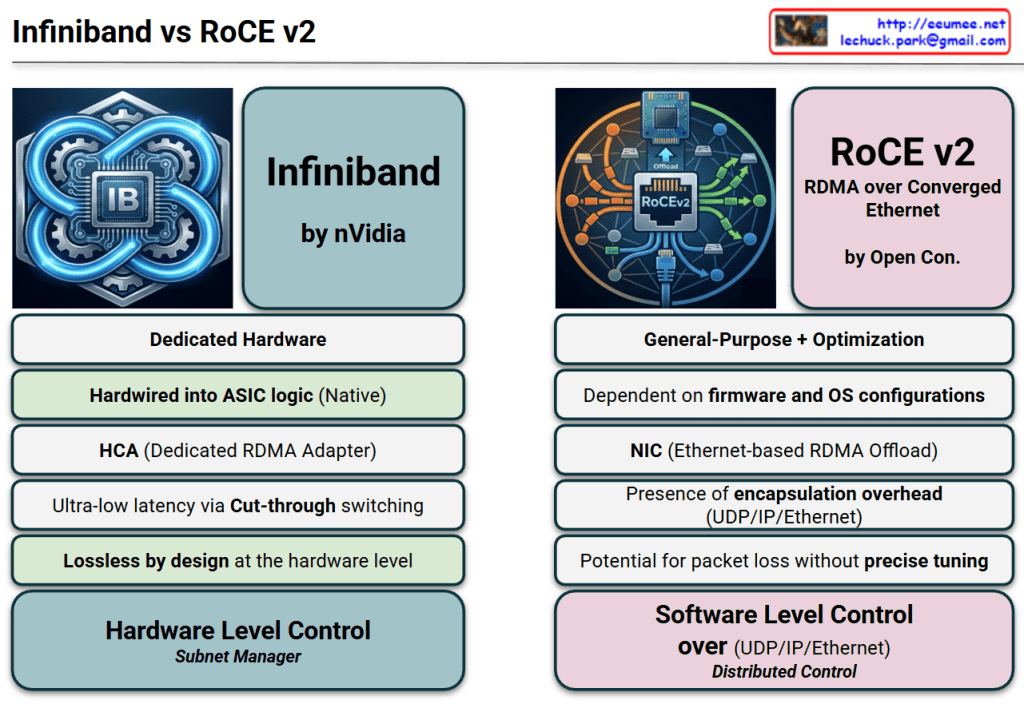
This image provides a technical comparison between InfiniBand and RoCE v2 (RDMA over Converged Ethernet), the two dominant networking protocols used in modern AI data centers and High-Performance Computing (HPC) environments.
1. Architectural Philosophy
- InfiniBand (Dedicated Hardware): Designed from the ground up specifically for high-throughput, low-latency communication. It is a proprietary ecosystem largely driven by NVIDIA (Mellanox).
- RoCE v2 (General-Purpose + Optimization): An evolution of standard Ethernet designed to bring RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) capabilities to traditional network infrastructures. It is backed by the Open Consortium.
2. Hardware vs. Software Logic
- Hardwired ASIC (InfiniBand): The protocol logic is baked directly into the silicon. This “Native” approach ensures consistent performance with minimal jitter.
- Firmware & OS Dependent (RoCE v2): Relies more heavily on the NIC’s firmware and operating system configurations, making it more flexible but potentially more complex to stabilize.
3. Data Transfer Efficiency
- Ultra-low Latency (InfiniBand): Utilizes Cut-through switching, where the switch starts forwarding the packet as soon as the destination address is read, without waiting for the full packet to arrive.
- Encapsulation Overhead (RoCE v2): Because it runs on Ethernet, it must wrap RDMA data in UDP/IP/Ethernet headers. This adds “overhead” (extra data bits) and processing time compared to the leaner InfiniBand frames.
4. Reliability and Loss Management
- Lossless by Design (InfiniBand): It uses a credit-based flow control mechanism at the hardware level, ensuring that a sender never transmits data unless the receiver has room to buffer it. This guarantees zero packet loss.
- Tuning-Dependent (RoCE v2): Ethernet is natively “lossy.” To make RoCE v2 work effectively, the network must be “Converged” using complex features like PFC (Priority Flow Control) and ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification). Without precise tuning, performance can collapse during congestion.
5. Network Management
- Subnet Manager (InfiniBand): Uses a centralized “Subnet Manager” to discover the topology and manage routing, which simplifies the management of massive GPU clusters.
- Distributed Control (RoCE v2): Functions like a traditional IP network where routing and control are distributed across the switches and routers.
Comparison Summary
| Feature | InfiniBand | RoCE v2 |
| Primary Driver | Performance & Stability | Cost-effectiveness & Compatibility |
| Complexity | Plug-and-play (within IB ecosystem) | Requires expert-level network tuning |
| Latency | Absolute Lowest | Low (but higher than IB) |
| Scalability | High (specifically for AI/HPC) | High (standard Ethernet scalability) |
Design & Logic: InfiniBand is a dedicated, hardware-native solution for ultra-low latency, whereas RoCE v2 adapts general-purpose Ethernet for RDMA through software-defined optimization and firmware.
Efficiency & Reliability: InfiniBand is “lossless by design” with minimal overhead via cut-through switching, while RoCE v2 incurs encapsulation overhead and requires precise network tuning to prevent packet loss.
Control & Management: InfiniBand utilizes centralized hardware-level management (Subnet Manager) for peak stability, while RoCE v2 relies on distributed software-level control over standard UDP/IP/Ethernet stacks.
#InfiniBand #RoCEv2 #RDMA #AIDataCenter #NetworkingArchitecture #NVIDIA #HighPerformanceComputing #GPUCluster #DataCenterDesign #Ethernet #AITraining