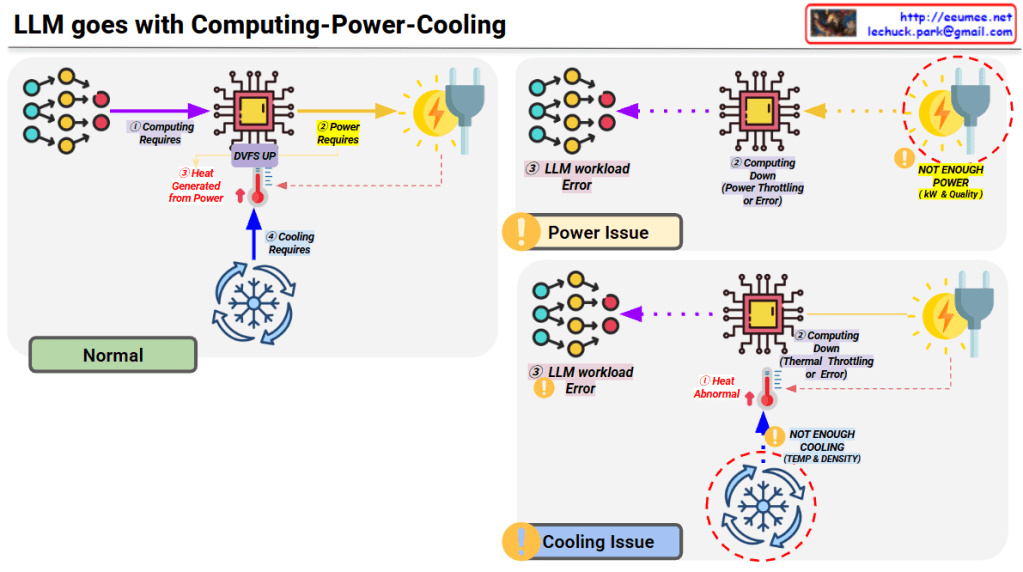
LLM’s Computing-Power-Cooling Relationship
This diagram illustrates the technical architecture and potential issues that can occur when operating LLMs (Large Language Models).
Normal Operation (Top Left)
- Computing Requires – LLM workload is delivered to the processor
- Power Requires – Power supplied via DVFS (Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling)
- Heat Generated – Heat is produced during computing processes
- Cooling Requires – Temperature management through proper cooling systems
Problem Scenarios
Power Issue (Top Right)
- Symptom: Insufficient power (kW & Quality)
- Results:
- Computing performance degradation
- Power throttling or errors
- LLM workload errors
Cooling Issue (Bottom Right)
- Symptom: Insufficient cooling (Temperature & Density)
- Results:
- Abnormal heat generation
- Thermal throttling or errors
- Computing performance degradation
- LLM workload errors
Key Message
For stable LLM operations, the three elements of Computing-Power-Cooling must be balanced. If any one element is insufficient, it leads to system-wide performance degradation or errors. This emphasizes that AI infrastructure design must consider not only computing power but also adequate power supply and cooling systems together.
Summary
- LLM operation requires a critical balance between computing, power supply, and cooling infrastructure.
- Insufficient power causes power throttling, while inadequate cooling leads to thermal throttling, both resulting in workload errors.
- Successful AI infrastructure design must holistically address all three components rather than focusing solely on computational capacity.
#LLM #AIInfrastructure #DataCenter #ThermalManagement #PowerManagement #AIOperations #MachineLearning #HPC #DataCenterCooling #AIHardware #ComputeOptimization #MLOps #TechInfrastructure #AIatScale #GreenAI
WIth Claude