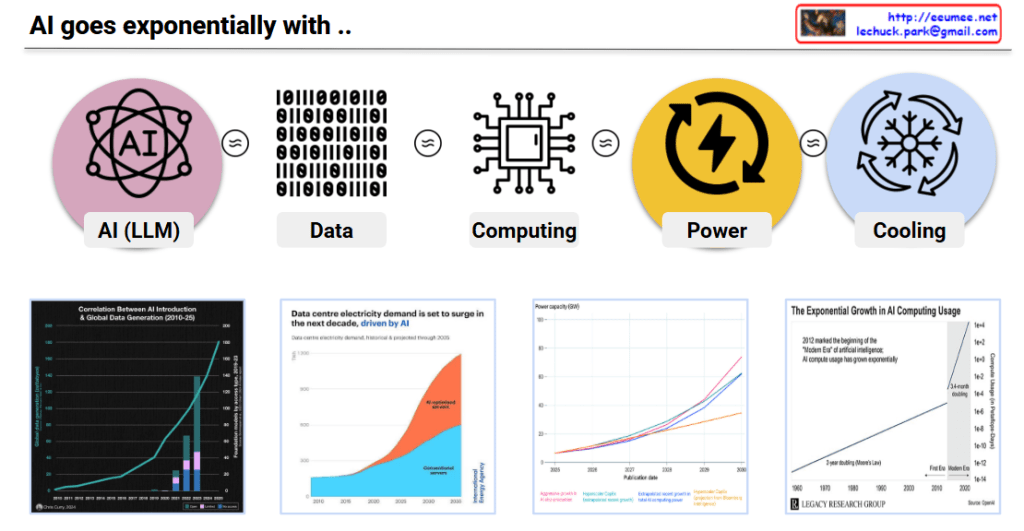
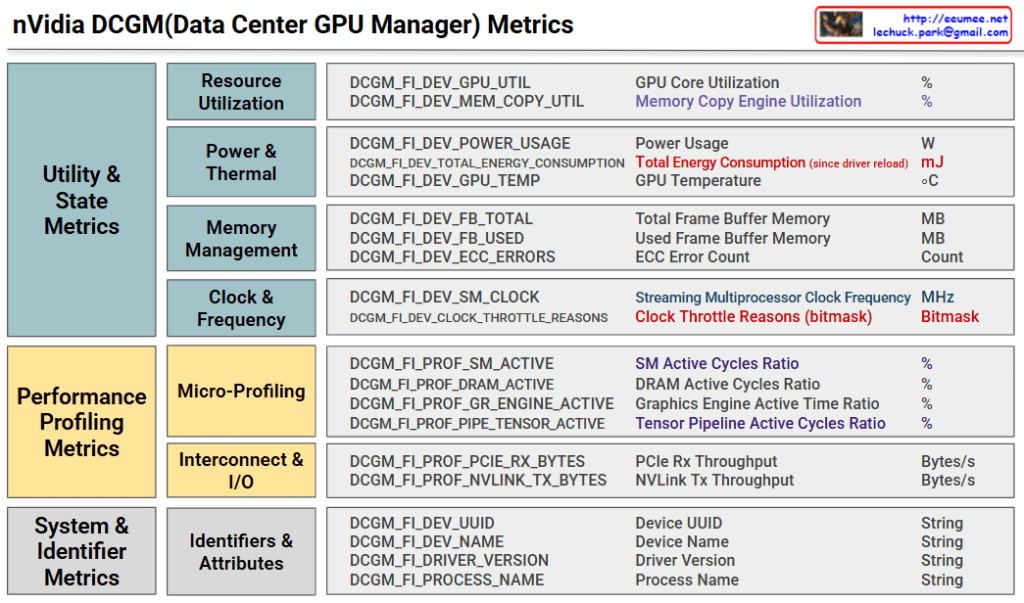
Power/Cooling Impacts on AI Work – Analysis
This slide summarizes research findings on how AI workloads impact power grids and cooling systems.
Key Findings:
📊 Reliability & Failure Studies
- Large-Scale ML Cluster Reliability (Meta, 2024/25)
- 1024-GPU job MTTF (Mean Time To Failure): 7.9 hours
- 8-GPU job: 47.7 days
- 16,384-GPU job: 1.8 hours
- → Larger jobs = higher failure risk due to cooling/power faults amplifying errors
🔌 Silent Data Corruption (SDC)
- SDC in LLM Training (2025)
- Meta report: 6 SDC failures in 54-day pretraining run
- Power droop, thermal stress → hardware faults → silent errors → training divergence
⚡ Inference Energy Efficiency
- LLM Inference Energy Consumption (2025)
- GPT-4o query benchmarks:
- Short: 0.43 Wh
- Medium: ~3.71 Wh
- Batch 4→8: ~43% savings
- Batch 8→16: ~43% savings per prompt
- → PUE & infrastructure efficiency significantly impact inference cost, delay, and carbon footprint
- GPT-4o query benchmarks:
🏭 Grid-Level Instability
- AI-Induced Power Grid Disruptions (2024)
- Model training causes power transients
- Dropouts → hardware resets
- Grid-level instability → node-level errors (SDC, restarts) → LLM job failures
🎯 Summary:
- Large-scale AI workloads face exponentially higher failure rates – bigger jobs are increasingly vulnerable to power/cooling system issues, with 16K-GPU jobs failing every 1.8 hours.
- Silent data corruption from thermal/power stress causes undetected training failures, while inference efficiency can be dramatically improved through batch optimization (43% energy reduction).
- AI training creates a vicious cycle of grid instability – power transients trigger hardware faults that cascade into training failures, requiring robust infrastructure design for power stability and fault tolerance.
#AIInfrastructure #MLOps #DataCenterEfficiency #PowerManagement #AIReliability #LLMTraining #SilentDataCorruption #EnergyEfficiency #GridStability #AIatScale #HPC #CoolingSystem #AIFailures #SustainableAI #InferenceOptimization
With Claude