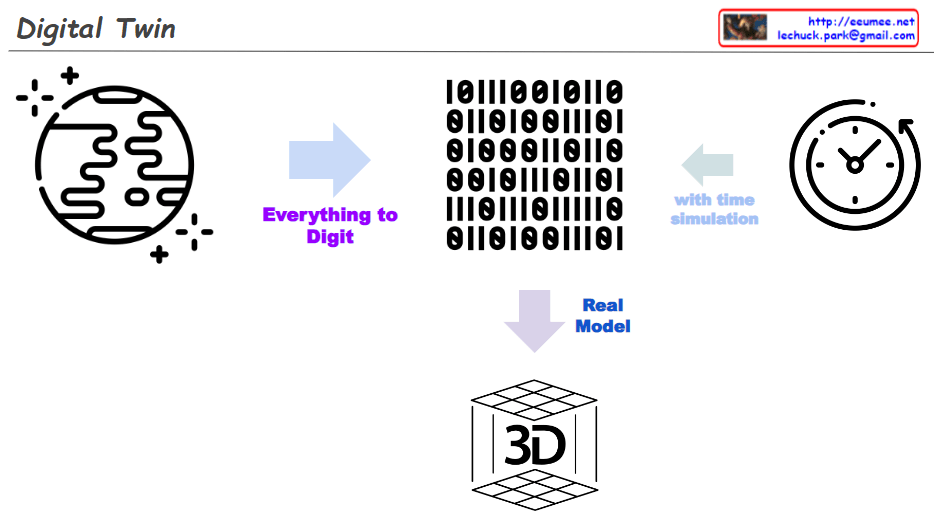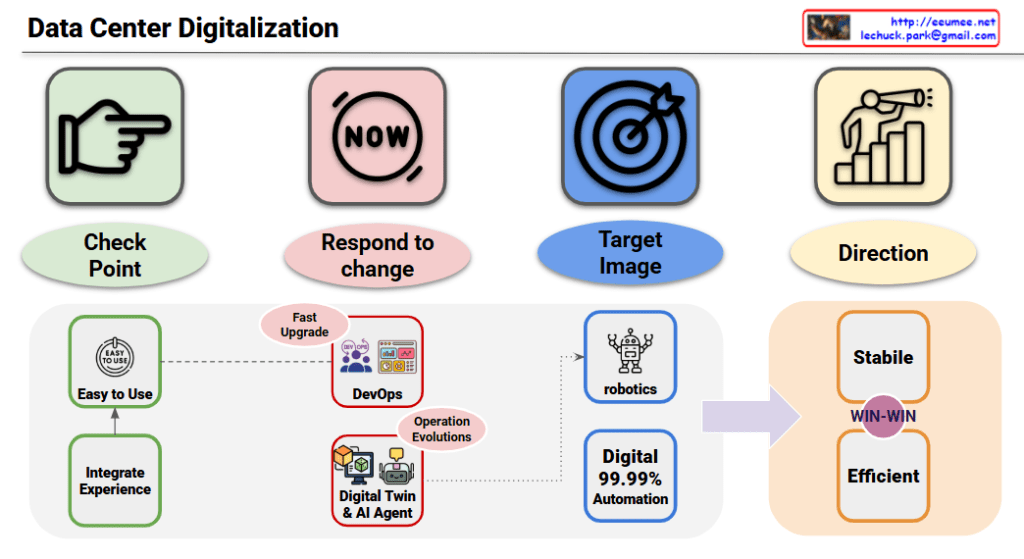
This image presents a roadmap for “Data Center Digitalization” showing the evolutionary process. Based on your explanation, here’s a more accurate interpretation:
Top 4 Core Concepts (Purpose for All Stages)
- Check Point: Current state inspection and verification point for each stage
- Respond to change: Rapid response system to quick changes
- Target Image: Final target state to be achieved
- Direction: Overall strategic direction setting
Digital Transformation Evolution Stages
Stage 1: Experience-Based Digital Environment Foundation
- Easy to Use: Creating user-friendly digital environments through experience
- Integrate Experience: Integrating existing data center operational experience and know-how into the digital environment
- Purpose: Utilizing existing operational experience as checkpoints to establish a foundation for responding to changes
Stage 2: DevOps Integrated Environment Configuration
- DevOps: Development-operations integrated environment supporting Fast Upgrade
- Building efficient development-operations integrated systems based on existing operational experience and know-how
- Purpose: Implementing DevOps environment that can rapidly respond to changes based on integrated experience
Stage 3: Evolution to Intelligent Digital Environment
- Digital Twin & AI Agent(LLM): Accumulated operational experience and know-how evolve into digital twins and AI agents
- Intelligent automated decision-making through Operation Evolutions
- Purpose: Establishing intelligent systems toward the target image and confirming operational direction
Stage 4: Complete Automation Environment Achievement
- Robotics: Unmanned operations through physical automation
- Digital 99.99% Automation: Nearly complete digital automation environment integrating all experience and know-how
- Purpose: Achieving the final target image – complete digital environment where all experience is implemented as automation
Final Goal: Simultaneous Development of Stability and Efficiency
WIN-WIN Achievement:
- Stable: Ensuring high availability and reliability based on accumulated operational experience
- Efficient: Maximizing operational efficiency utilizing integrated know-how
This diagram presents a strategic roadmap where data centers systematically integrate existing operational experience and know-how into digital environments, evolving step by step while reflecting the top 4 core concepts as purposes for each stage, ultimately achieving both stability and efficiency simultaneously.
With Claude