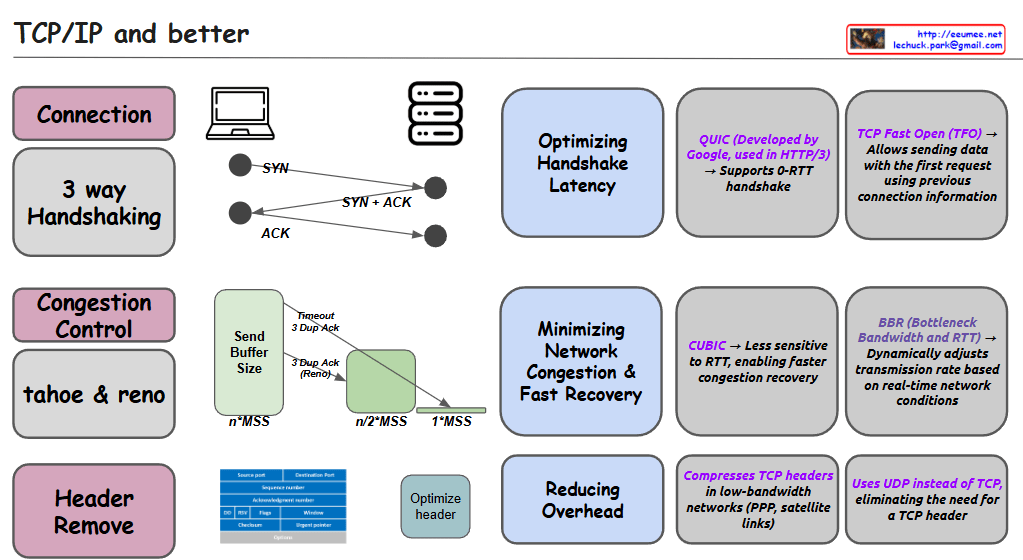
This image is an informational diagram titled “TCP/IP and better” that explains various aspects of network protocols and optimizations.
The diagram is organized into three main sections:
- Connection
- Shows “3 way Handshaking” with a visual representation of the SYN, SYN+ACK, ACK sequence
- “Optimizing Handshake Latency” section mentions:
- QUIC (Developed by Google, used in HTTP/3) → Supports 0-RTT handshake
- TCP Fast Open (TFO) → Allows sending data with the first request using previous connection information
- Congestion Control
- Lists “tahoe & reno” congestion control algorithms
- Shows diagrams of Send Buffer Size with concepts like “Timeout 3-Dup-Ack” and “3-Dup Ack (Reno)”
- “Minimizing Network Congestion & Fast Recovery” section mentions:
- CUBIC → Less sensitive to RTT, enabling faster congestion recovery
- BBR (Bottleneck Bandwidth and RTT) → Dynamically adjusts transmission rate based on real-time network conditions
- Header Remove
- Shows TCP header structure diagram and “Optimize header” section
- “Reducing Overhead” section mentions:
- Compresses TCP headers in low-bandwidth networks (PPP, satellite links)
- Uses UDP instead of TCP, eliminating the need for a TCP header
The diagram appears to be an educational resource about TCP/IP protocols and various optimizations that have been developed to improve network performance, particularly focused on connection establishment, congestion control, and overhead reduction.
With Claude