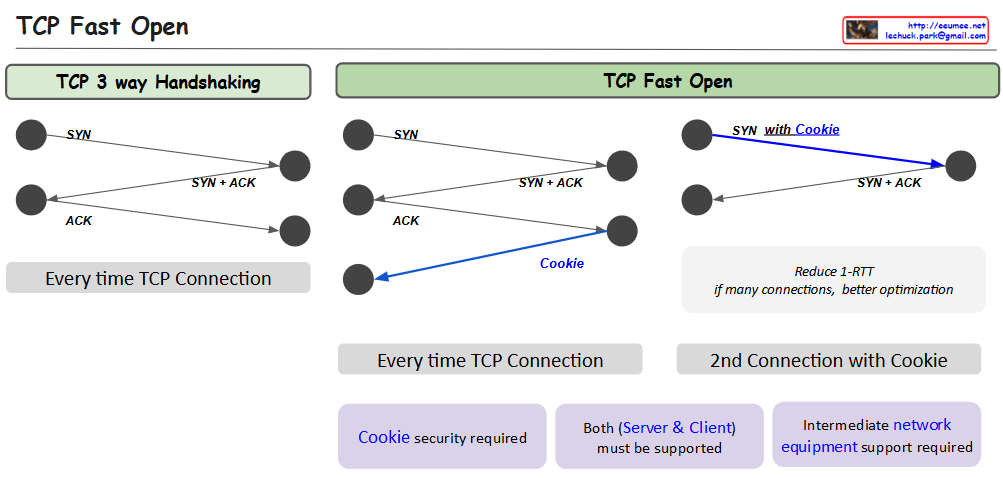
The image compares two TCP connection establishment methods:
- TCP 3-Way Handshaking (Traditional Method):
- Shows a standard connection process with three steps:
- SYN (Synchronize) packet sent
- SYN + ACK (Synchronize + Acknowledge) packet returned
- ACK (Acknowledge) packet sent back
- This happens every time a new TCP connection is established
- Requires a full round-trip time (RTT) for connection setup
- TCP Fast Open:
- Introduces a “Cookie” mechanism to optimize connection establishment
- First connection follows the traditional 3-way handshake
- Subsequent connections can use the stored cookie to reduce connection time
- Benefits:
- Reduces Round-Trip Time (1-RTT)
- Better optimization for multiple connections
- Requirements for TCP Fast Open:
- Cookie security must be implemented
- Both server and client must support the method
- Intermediate network equipment must support the technique
The blue arrows in the TCP Fast Open diagram represent the cookie exchange and optimized connection process, highlighting the key difference from the traditional method.
With Claude






