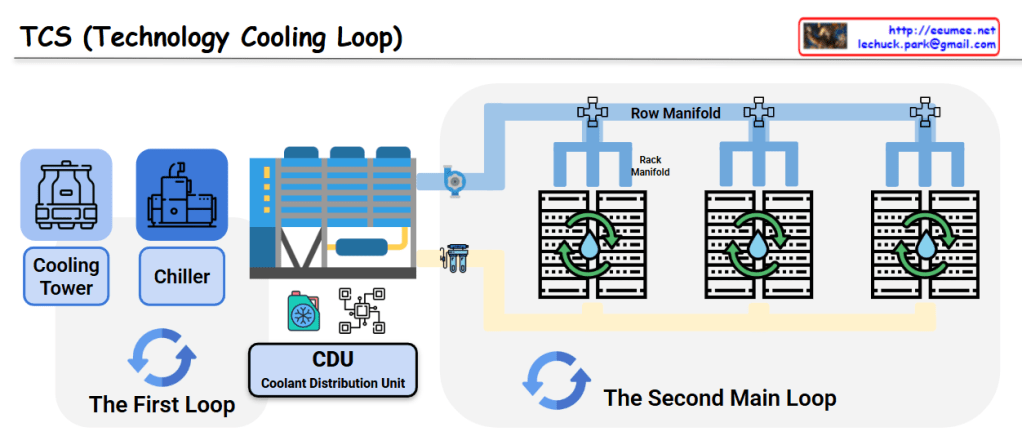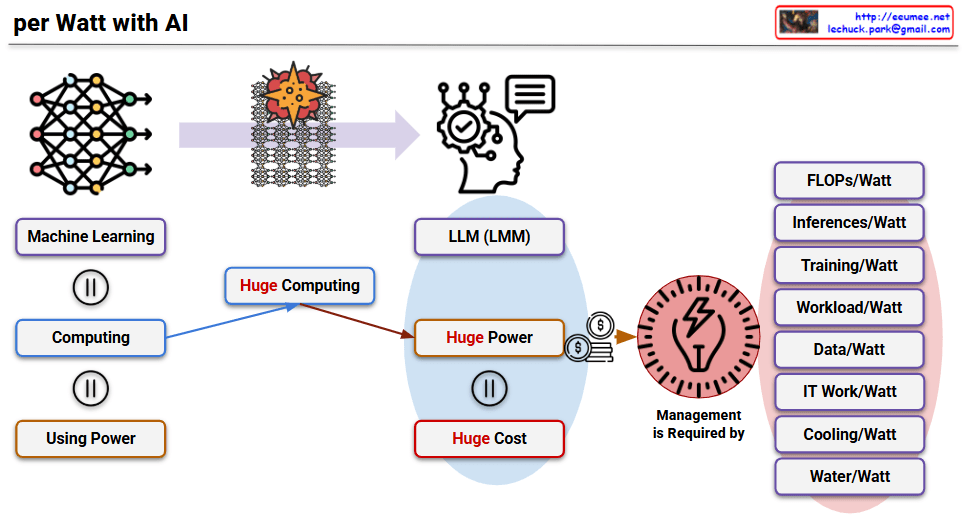
This image titled “per Watt with AI” is a diagram explaining the paradigm shift in power efficiency following the AI era, particularly after the emergence of LLMs.
Overall Context
Core Structure of AI Development:
- Machine Learning = Computing = Using Power
- The equal signs (=) indicate that these three elements are essentially the same concept. In other words, AI machine learning inherently means large-scale computing, which inevitably involves power consumption.
Characteristics of LLMs: As AI, particularly LLMs, have proven their effectiveness, tremendous progress has been made. However, due to their technical characteristics, they have the following structure:
- Huge Computing: Massively parallel processing of simple tasks
- Huge Power: Enormous power consumption due to this parallel processing
- Huge Cost: Power costs and infrastructure expenses
Importance of Power Efficiency Metrics
With hardware advancements making this approach practically effective, power consumption has become a critical issue affecting even the global ecosystem. Therefore, power is now used as a performance indicator for all operations.
Key Power Efficiency Metrics
Performance-related:
- FLOPs/Watt: Floating-point operations per watt
- Inferences/Watt: Number of inferences processed per watt
- Training/Watt: Training performance per watt
Operations-related:
- Workload/Watt: Workload processing capacity per watt
- Data/Watt: Data processing capacity per watt
- IT Work/Watt: IT work processing capacity per watt
Infrastructure-related:
- Cooling/Watt: Cooling efficiency per watt
- Water/Watt: Water usage efficiency per watt
This diagram illustrates that in the AI era, power efficiency has become the core criterion for all performance evaluations, transcending simple technical metrics to encompass environmental, economic, and social perspectives.
With Claude