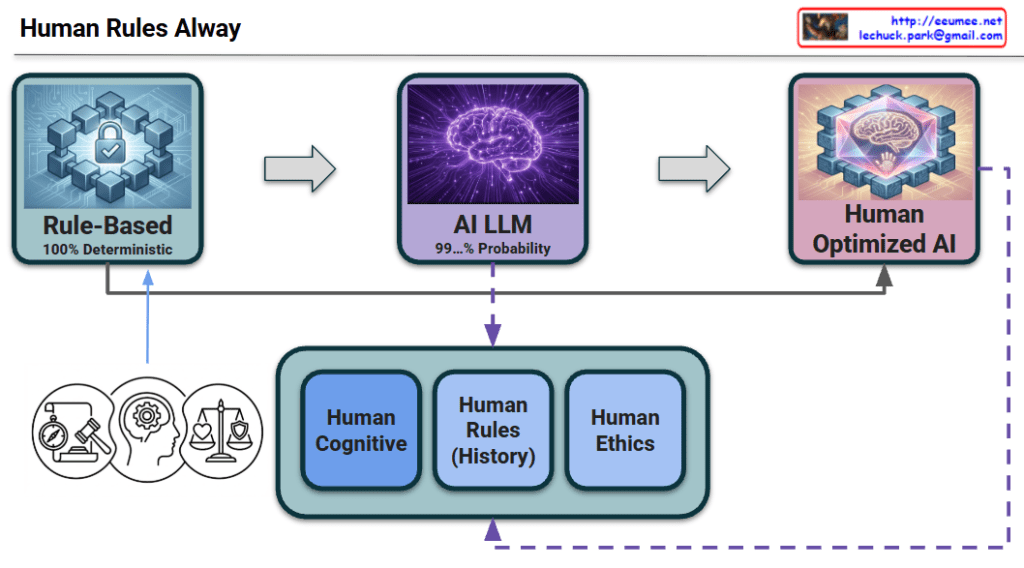
The Evolutionary Roadmap to Human-Optimized AI
This diagram visualizes the history and future direction of intelligent systems. It illustrates the evolution from the era of manual programming to the current age of generative AI, and finally to the ultimate goal where human standards perfect the technology.
1. The 3 Stages of Technological Evolution (Top Flow)
- Stage 1: Rule-Based (The Foundation / Past)
- Concept: “The Era of Human-Defined Logic”
- Context: This represents the starting point of computing where humans explicitly created formulas and coded every rule.
- Characteristics: It is 100% Deterministic. While accurate within its scope, it cannot handle the complexity of the real world beyond what humans have manually programmed.
- Stage 2: AI LLM (The Transition / Present)
- Concept: “The Era of Probabilistic Scale”
- Context: We have evolved into the age of massive parallel processing and Large Language Models.
- Characteristics: It operates on 99…% Probability. It offers immense scalability and creativity that rule-based systems could never achieve, but it lacks the absolute certainty of the past, occasionally leading to inefficiencies or hallucinations.
- Stage 3: Human Optimized AI (The Final Goal / Future)
- Concept: “The Era of Reliability & Efficiency”
- Context: This is the destination we must reach. It is not just about using AI, but about integrating the massive power of the “Present” (AI LLM) with the precision of the “Past” (Rule-Based).
- Characteristics: By applying human standards to control the AI’s massive parallel processing, we achieve a system that is both computationally efficient and strictly reliable.
2. The Engine of Evolution: Human Standards (Bottom Box)
This section represents the mechanism that drives the evolution from Stage 2 to Stage 3.
- The Problem: Raw AI (Stage 2) consumes vast energy and can be unpredictable.
- The Solution: We must re-introduce the “Human Rules” (History, Logic, Ethics) established in Stage 1 into the AI’s workflow.
- The Process:
- Constraint & Optimization: Human Cognition and Rules act as a pruning mechanism, cutting off wasteful parallel computations in the LLM.
- Safety: Ethics ensure the output aligns with human values.
- Result: This filtering process transforms the raw, probabilistic energy of the LLM into the polished, “Human Optimized” state.
3. The Feedback Loop (Continuous Evolution)
- Dashed Line: The journey doesn’t end at Stage 3. The output from the optimized AI is reviewed by humans, which in turn updates our rules and ethical standards. This circular structure ensures that the AI continues to evolve alongside human civilization.
This diagram declares that the future of AI lies not in discarding the old “Rule-Based” ways, but in fusing that deterministic precision with modern probabilistic power to create a truly optimized intelligence.
#AIEvolution #FutureOfAI #HybridAI #DeterministicVsProbabilistic #HumanInTheLoop #TechRoadmap #AIArchitecture #Optimization #ResponsibleAI