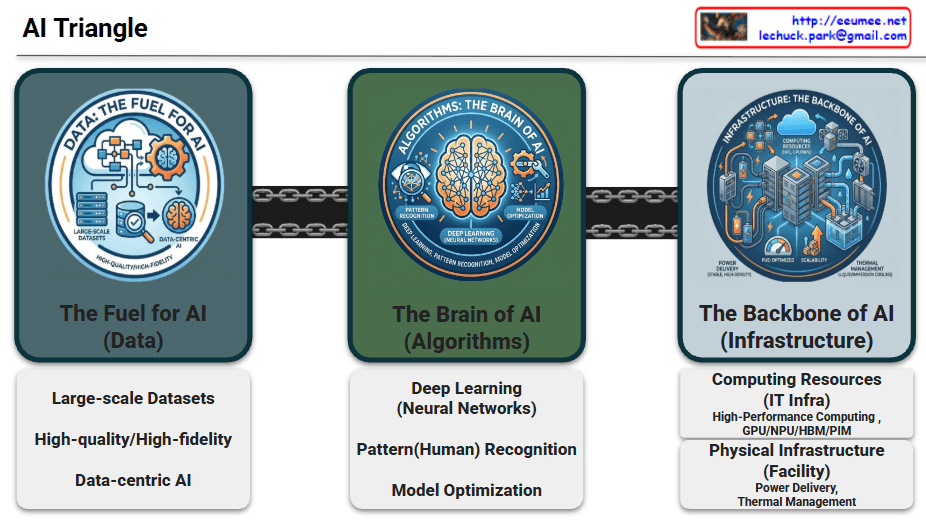
📐 The AI Triangle: Core Pillars of Evolution
1. Data: The Fuel for AI
Data serves as the essential raw material that determines the intelligence and accuracy of AI models.
- Large-scale Datasets: Massive volumes of information required for foundational training.
- High-quality/High-fidelity: The emphasis on clean, accurate, and reliable data to ensure superior model performance.
- Data-centric AI: A paradigm shift focusing on enhancing data quality rather than just iterating on model code.
2. Algorithms: The Brain of AI
Algorithms provide the logical framework and mathematical structures that allow machines to learn from data.
- Deep Learning (Neural Networks): Multi-layered architectures inspired by the human brain to process complex information.
- Pattern Recognition: The ability to identify hidden correlations and make predictions from raw inputs.
- Model Optimization: Techniques to improve efficiency, reduce latency, and minimize computational costs.
3. Infrastructure: The Backbone of AI
The physical and digital foundation that enables massive computations and ensures system stability.
- Computing Resources (IT Infra):
- HPC & Accelerators: High-performance clusters utilizing GPUs, NPUs, and HBM/PIM for parallel processing.
- Physical Infrastructure (Facilities):
- Power Delivery: Reliable, high-density power systems including UPS, PDU, and smart energy management.
- Thermal Management: Advanced cooling solutions like Liquid Cooling and Immersion Cooling to handle extreme heat from AI chips.
- Scalability & PUE: Focus on sustainable growth and maximizing energy efficiency (Power Usage Effectiveness).
📝 Summary
- The AI Triangle represents the vital synergy between high-quality Data, sophisticated Algorithms, and robust Infrastructure.
- While data fuels the model and algorithms provide the logic, infrastructure acts as the essential backbone that supports massive scaling and operational reliability.
- Modern AI evolution increasingly relies on advanced facility management, specifically optimized power delivery and high-efficiency cooling, to sustain next-generation workloads.
#AITriangle #AIInfrastructure #DataCenter #DeepLearning #GPU #LiquidCooling #DataCentric #Sustainability #PUE #TechArchitecture
With Gemini