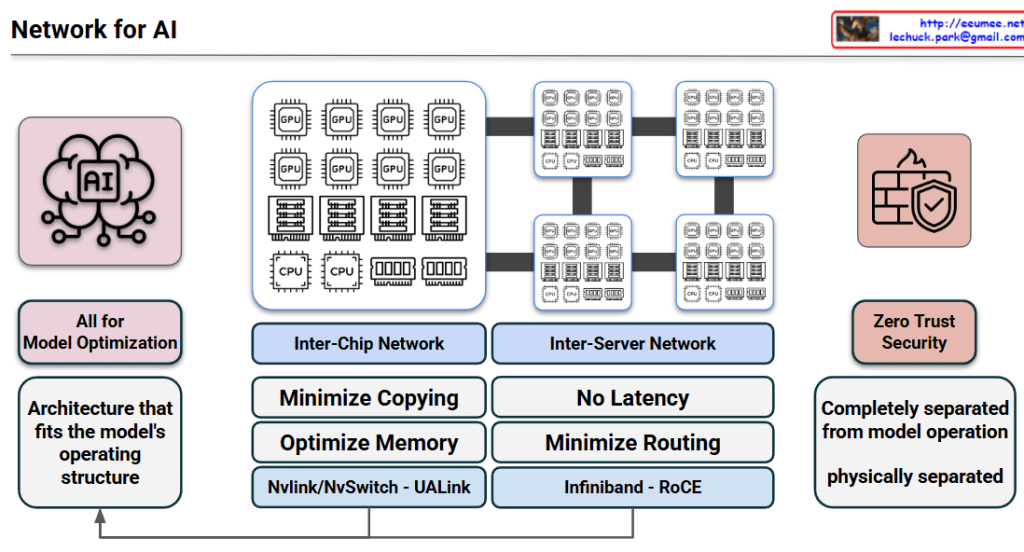
1. Core Philosophy: All for Model Optimization
The primary goal is to create an “Architecture that fits the model’s operating structure.” Unlike traditional general-purpose data centers, AI infrastructure is specialized to handle the massive data throughput and synchronized computations required by LLMs (Large Language Models).
2. Hierarchical Network Design
The architecture is divided into two critical layers to handle different levels of data exchange:
A. Inter-Chip Network (Scale-Up)
This layer focuses on the communication between individual GPUs/Accelerators within a single server or node.
- Key Goals: Minimize data copying and optimize memory utilization (Shared Memory/Memory Pooling).
- Technologies: * NVLink / NVSwitch: NVIDIA’s proprietary high-speed interconnect.
- UALink (Ultra Accelerator Link): The new open standard designed for scale-up AI clusters.
B. Inter-Server Network (Scale-Out)
This layer connects multiple server nodes to form a massive AI cluster.
- Key Goals: Achieve “No Latency” (Ultra-low latency) and minimize routing overhead to prevent bottlenecks during collective communications (e.g., All-Reduce).
- Technologies: * InfiniBand: A lossless, high-bandwidth fabric preferred for its low CPU overhead.
- RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet): High-speed Ethernet that allows direct memory access between servers.
3. Zero Trust Security & Physical Separation
A unique aspect of this architecture is the treatment of security.
- Operational Isolation: The security and management plane is completely separated from the model operation plane.
- Performance Integrity: By being physically separated, security protocols (like firewalls or encryption inspection) do not introduce latency into the high-speed compute fabric where the model runs. This ensures that a “Zero Trust” posture does not degrade training or inference speed.
4. Architectural Feedback Loop
The arrow at the bottom indicates a feedback loop: the performance metrics and requirements of the inter-chip and inter-server networks directly inform the ongoing optimization of the overall architecture. This ensures the platform evolves alongside advancing AI model structures.
The architecture prioritizes model-centric optimization, ensuring infrastructure is purpose-built to match the specific operating requirements of large-scale AI workloads.
It employs a dual-tier network strategy using Inter-chip (NVLink/UALink) for memory efficiency and Inter-server (InfiniBand/RoCE) for ultra-low latency cluster scaling.
Zero Trust security is integrated through complete physical separation from the compute fabric, allowing for robust protection without causing any performance bottlenecks.
#AIDC #ArtificialIntelligence #GPU #Networking #NVLink #UALink #InfiniBand #RoCEv2 #ZeroTrust #DataCenterArchitecture #MachineLearningOps #ScaleOut
