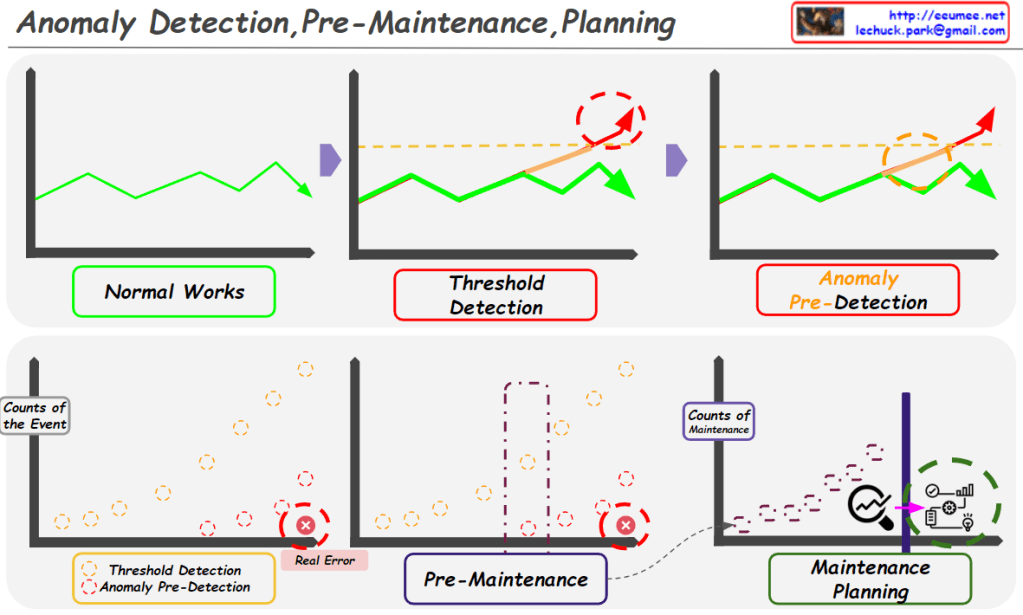
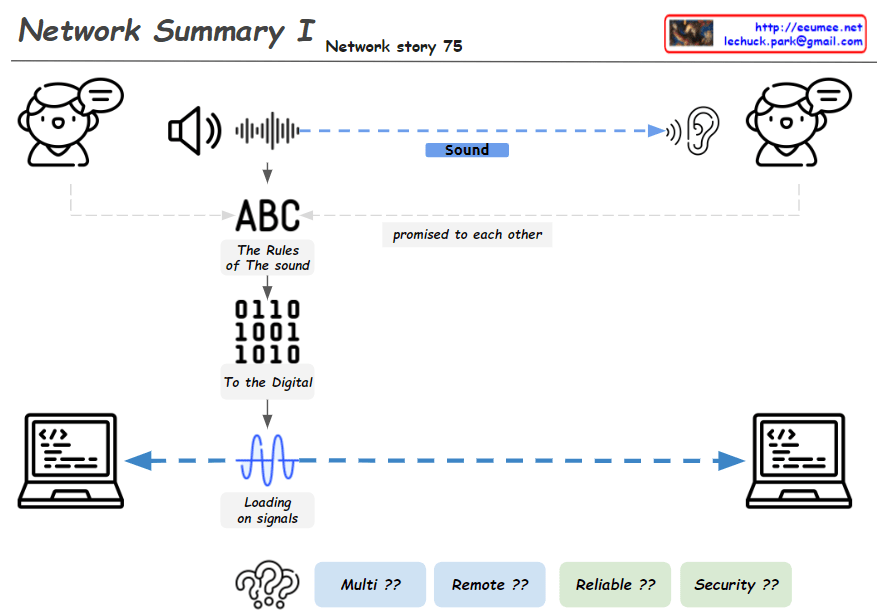
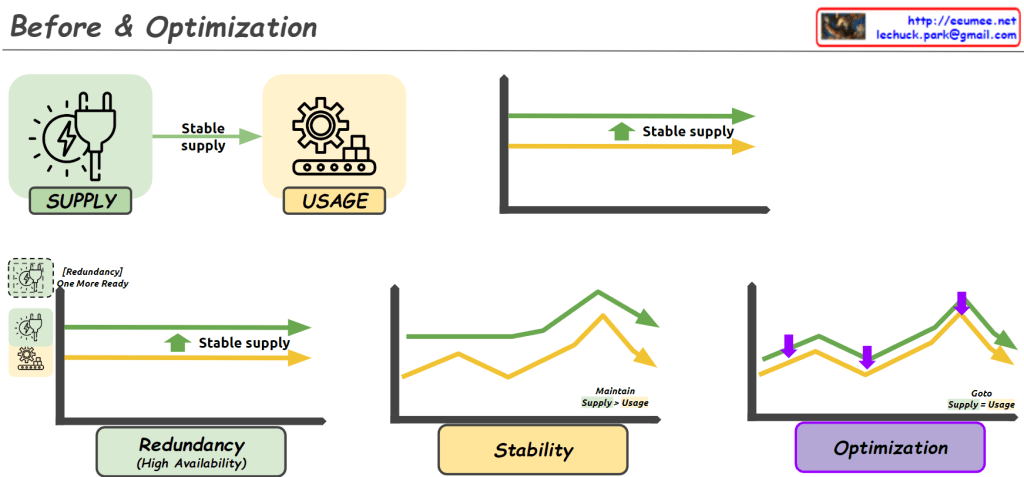
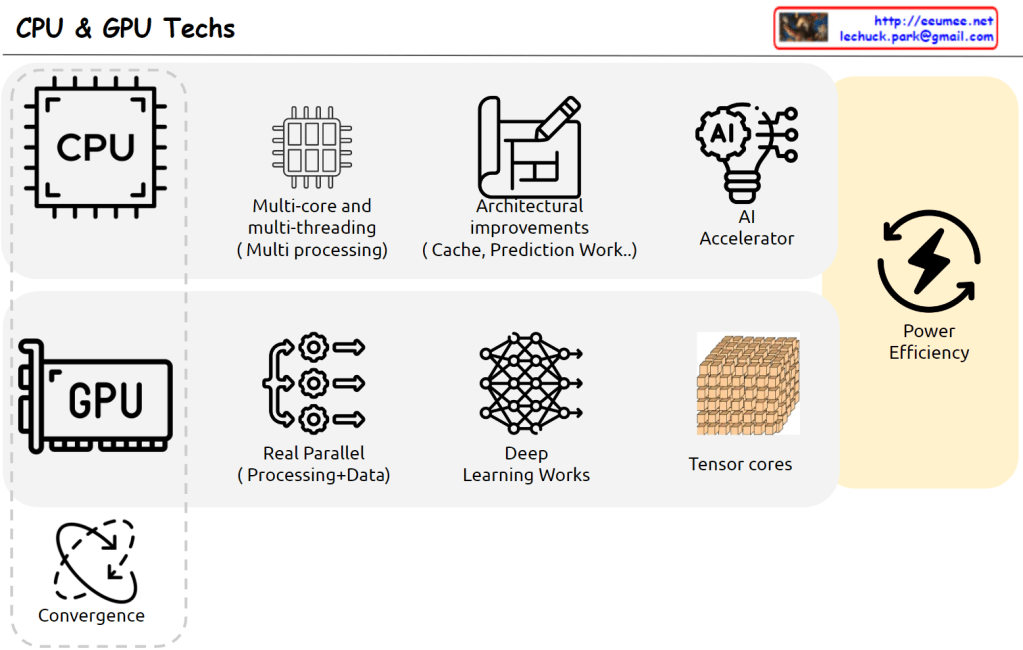
From Claude with some prompting
This image illustrates different architectures of Parallel Processing:
- Single Core CPU: A single CPU connected to memory via one memory channel. The memory is divided into Instruction (Computing) and Data sections.
- Multi Core CPU: A CPU with multiple cores connected to memory through multiple memory channels. The memory structure is similar to the single core setup.
- NUMA (Non-Uniform Memory Access): Multiple multi-core CPUs, each with local memory. CPUs can access memory attached to other CPUs, but with “More Hop Memory Access”.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): Described as “Completely Independent Processing-Memory Units”. It uses High Bandwidth Memory and has a large number of processing units directly mapped to data.
The GPU architecture shows many small processing units connected to a shared high-bandwidth memory, illustrating its capacity for massive parallel processing.
This diagram effectively contrasts CPU and GPU architectures, highlighting how CPUs are optimized for sequential processing while GPUs are designed for highly parallel tasks.