Data Accumulation Perspective
History → Internet: All knowledge and information accumulated throughout human history is digitized through the internet and converted into AI training data. This consists of multimodal data including text, images, audio, and other formats.
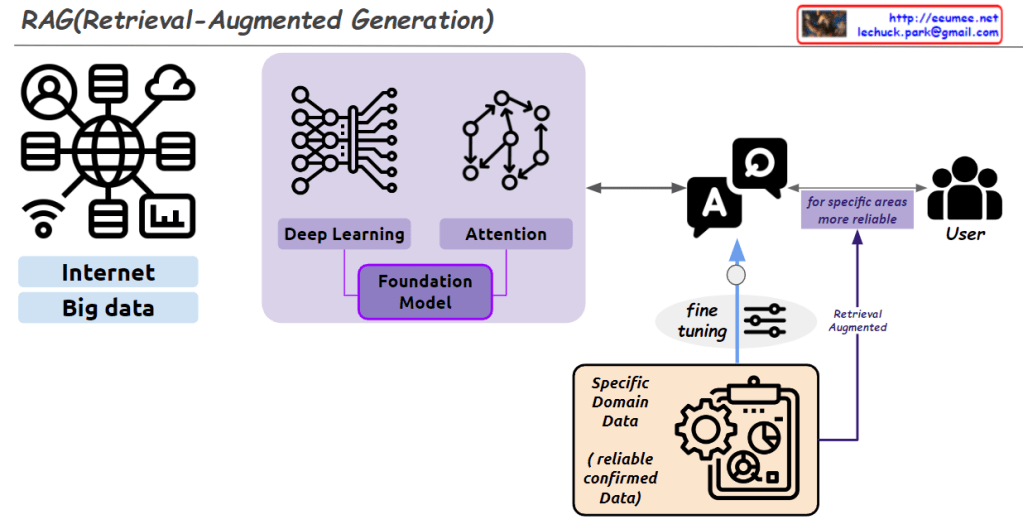
Foundation Model: Large language models (LLMs) and multimodal models are pre-trained based on this vast accumulated data. Examples include GPT, BERT, CLIP, and similar architectures.
Human to AI: Applying Human Cognitive Patterns to AI
1. Chain of Thoughts
- Implementation of human logical reasoning processes in the Reasoning stage
- Mimicking human cognitive patterns that break down complex problems into step-by-step solutions
- Replicating the human approach of “think → analyze → conclude” in AI systems
2. Mixture of Experts
- AI implementation of human expert collaboration systems utilized in the Experts domain
- Architecting the way human specialists collaborate on complex problems into model structures
- Applying the human method of synthesizing multiple expert opinions for problem-solving into AI
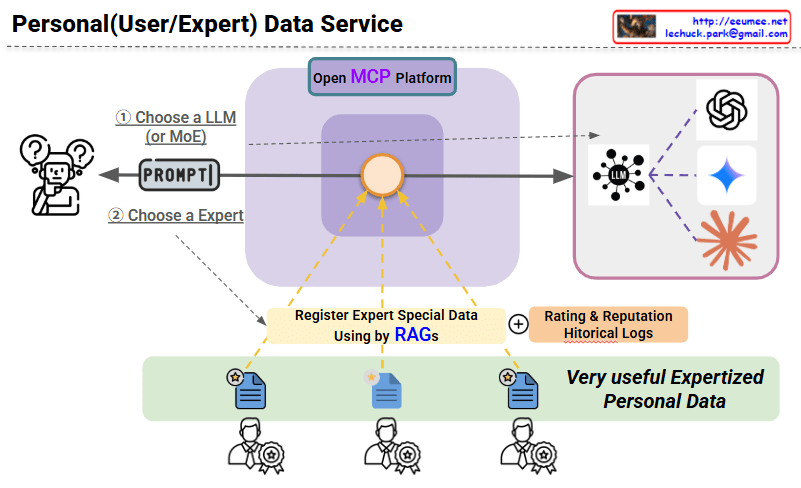
3. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Implementing the human process of searching existing knowledge → generating new responses into AI systems
- Systematizing the human approach of “reference material search → comprehensive judgment”
Personal/Enterprise/Sovereign Data Utilization
1. Personal Level
- Utilizing individual documents, history, preferences, and private data in RAG systems
- Providing personalized AI assistants and customized services
2. Enterprise Level
- Integrating organizational internal documents, processes, and business data into RAG systems
- Implementing enterprise-specific AI solutions and workflow automation
3. Sovereign Level
- Connecting national or regional strategic data to RAG systems
- Optimizing national security, policy decisions, and public services
Overall Significance: This architecture represents a Human-Centric AI system that transplants human cognitive abilities and thinking patterns into AI while utilizing multi-layered data from personal to national levels to evolve general-purpose AI (Foundation Models) into intelligent systems specialized for each level. It goes beyond simple data processing to implement human thinking methodologies themselves into next-generation AI systems.
With Claude