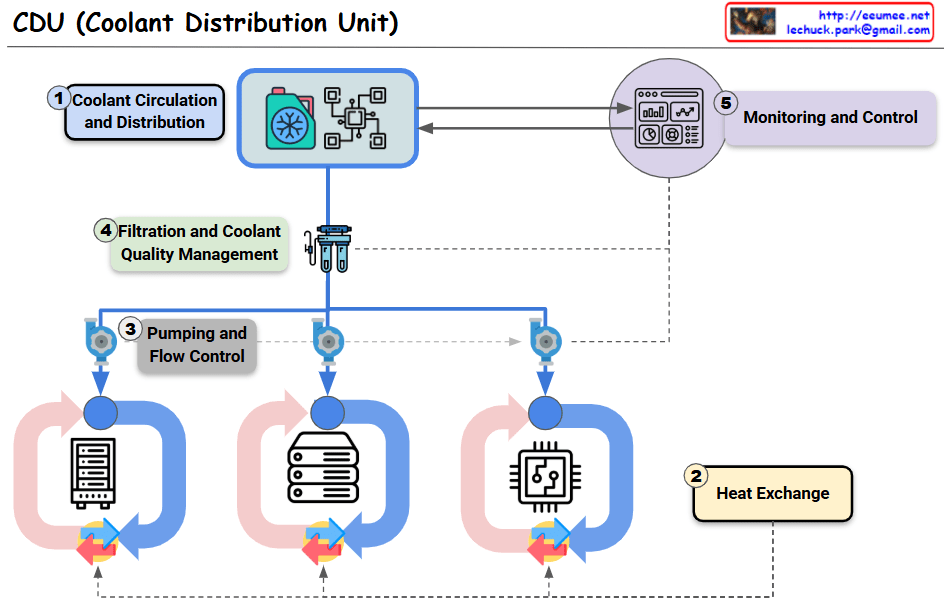
This image illustrates a Coolant Distribution Unit (CDU) with its key components and the liquid cooling system implemented in modern AI data centers. The diagram shows five primary components:
- Coolant Circulation and Distribution: The central component that efficiently distributes liquid coolant throughout the entire system.
- Heat Exchange: This section removes heat absorbed by the liquid coolant to maintain the cooling system’s efficiency.
- Pumping and Flow Control: Includes pumps and control devices that precisely manage the movement of coolant throughout the system.
- Filtration and Coolant Quality Management: A filtration system that purifies the liquid coolant and maintains optimal quality for cooling efficiency.
- Monitoring and Control: An interface that provides real-time monitoring and control of the entire liquid cooling system.
The three devices shown at the bottom of the diagram represent different levels of liquid cooling application in modern AI data centers:
- Rack-level liquid cooling
- Individual server-level liquid cooling
- Direct processor (CPU/GPU) chip-level liquid cooling
This diagram demonstrates how advanced liquid cooling technology has evolved from traditional air cooling methods to effectively manage the high heat generated in AI-intensive modern data centers. It shows an integrated approach where the CDU facilitates coolant circulation to efficiently remove heat at rack, server, and chip levels.
With Claude