Technical Analysis: The Impact of AI Loads on Weak Grids
1. The Problem: A Threat to Grid Stability
Large-scale AI loads combined with “Weak Grids” (where the Short Circuit Ratio, or SCR, is less than 3) significantly threaten power grid stability.
- AI Workload Characteristics: These loads are defined by sudden “Step Power Changes” and “Pulse-type Profiles” rather than steady consumption.
- Sensitivity: NERC (2025) warns that the decrease in voltage-sensitive loads and the rise of periodic workloads are major drivers of grid instability.
2. The Vicious Cycle of Instability
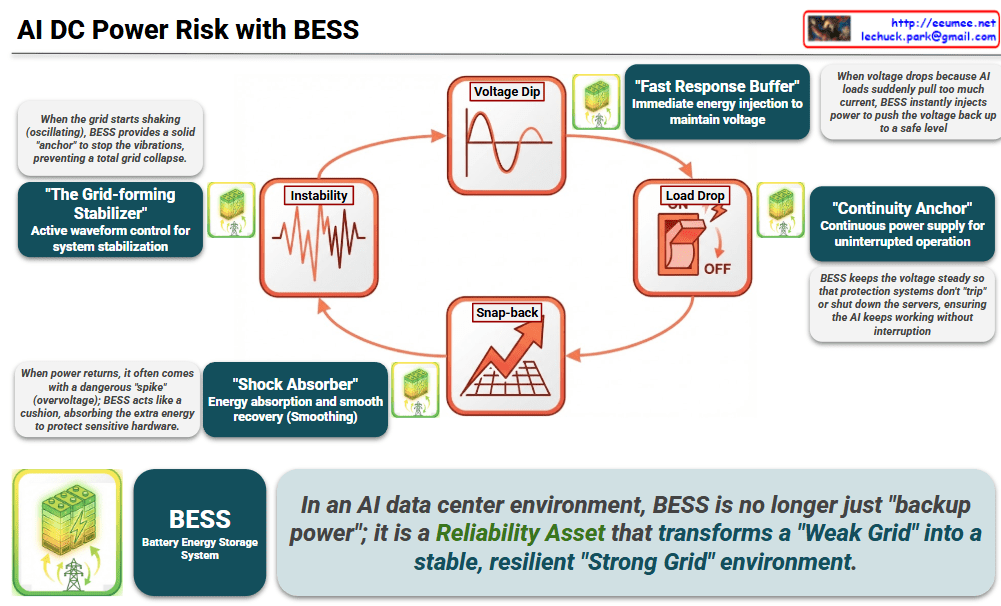
The images illustrate a four-stage downward spiral triggered by the interaction between AI hardware and a fragile power infrastructure:
- Voltage Dip: As AI loads suddenly spike, the grid’s high impedance causes a temporary but sharp drop in voltage levels. This degrades #PowerQuality and causes #VoltageSag.
- Load Drop: When voltage falls too low, protection systems trigger a sudden disconnection of the load ($P \rightarrow 0$). This leads to #ServiceDowntime and massive #LoadShedding.
- Snap-back: As the grid tries to recover or the load re-engages, there is a rapid and sudden power surge. This creates dangerous #Overvoltage and #SurgeInflow.
- Instability: The repetition of these fluctuations leads to waveform distortion and oscillation. Eventually, this causes #GridCollapse and a total #LossOfControl.
3. The Solution: BESS as a Reliability Asset
The final analysis reveals that a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) acts as the critical circuit breaker for this vicious cycle.
- Fast Response Buffer: BESS provides immediate energy injection the moment a dip is detected, maintaining voltage levels.
- Continuity Anchor: By holding the voltage steady, it prevents protection systems from “tripping,” ensuring uninterrupted operation for AI servers.
- Shock Absorber: During power recovery, BESS absorbs excess energy to “smooth” the transition and protect sensitive hardware from spikes.
- The Grid-forming Stabilizer: It uses active waveform control to stop oscillations, providing the “virtual inertia” needed to prevent total grid collapse.
Summary
- AI Load Dynamics: The erratic “pulse” nature of AI power consumption acts as a physical shock to weak grids, necessitating a new layer of protection.
- Beyond Backup Power: In this context, BESS is redefined as a Reliability Asset that transforms a “Weak Grid” into a resilient “Strong Grid” environment.
- Operational Continuity: By filling gaps, absorbing shocks, and anchoring the grid, BESS ensures that AI data centers remain operational even during severe transient events.
#BESS #GridStability #AIDataCenter #PowerQuality #WeakGrid #EnergyStorage #NERC2025 #VoltageSag #VirtualInertia #TechInfrastructure
with Gemini
