AI Data Center Power Efficiency Analysis
The Power Design Dilemma in AI Data Centers
AI data centers, comprised of power-hungry GPU clusters and high-performance servers, face critical decisions where power efficiency directly impacts operational costs and performance capabilities.
The Need for High-Voltage Distribution Systems
- AI Workload Characteristics: GPU training operations consume hundreds of kilowatts to megawatts continuously
- Power Density: High power density of 50-100kW per rack demands efficient power transmission
- Scalability: Rapid power demand growth following AI model size expansion
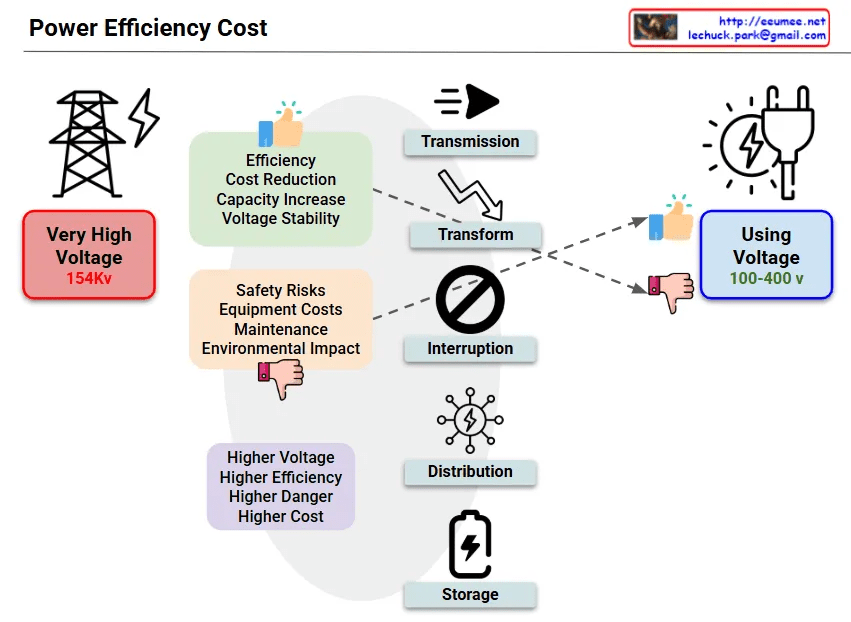
Efficiency vs Complexity Trade-offs
Advantages (Efficiency Perspective):
- Minimized Power Losses: High-voltage transmission dramatically reduces I²R losses (potential 20-30% power cost savings)
- Cooling Efficiency: Reduced power losses mean less heat generation, lowering cooling costs
- Infrastructure Investment Optimization: Fewer, larger cables can deliver massive power capacity
Disadvantages (Operational Complexity):
- Safety Risks: High-voltage equipment requires specialized expertise, increased accident risks
- Capital Investment: Expensive high-voltage transformers, switchgear, and protection equipment
- Maintenance Complexity: Specialized technical staff required, extended downtime during outages
- Regulatory Compliance: Complex permitting processes for electrical safety and environmental impact
AI DC Power Architecture Design Strategy
- Medium-Voltage Distribution: 13.8kV → 480V stepped transformation balancing efficiency and safety
- Modularization: Pod-based power delivery for operational flexibility
- Redundant Backup Systems: UPS and generator redundancy preventing AI training interruptions
- Smart Monitoring: Real-time power quality surveillance for proactive fault prevention
Financial Impact Analysis
- CAPEX: 15-25%(?) higher initial investment for high-voltage infrastructure
- OPEX: 20-35%(?) reduction in power and cooling costs over facility lifetime
- ROI: Typically 18-24(?) months payback period for hyperscale AI facilities
Conclusion
AI data centers must identify the optimal balance between power efficiency and operational stability. This requires prioritizing long-term operational efficiency over initial capital costs, making strategic investments in sophisticated power infrastructure that can support the exponential growth of AI computational demands while maintaining grid-level reliability and safety standards.
with Claude


