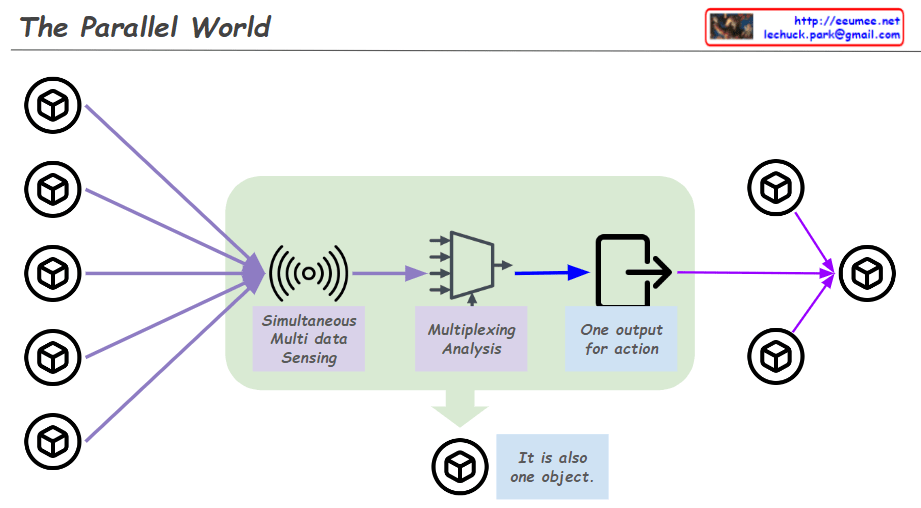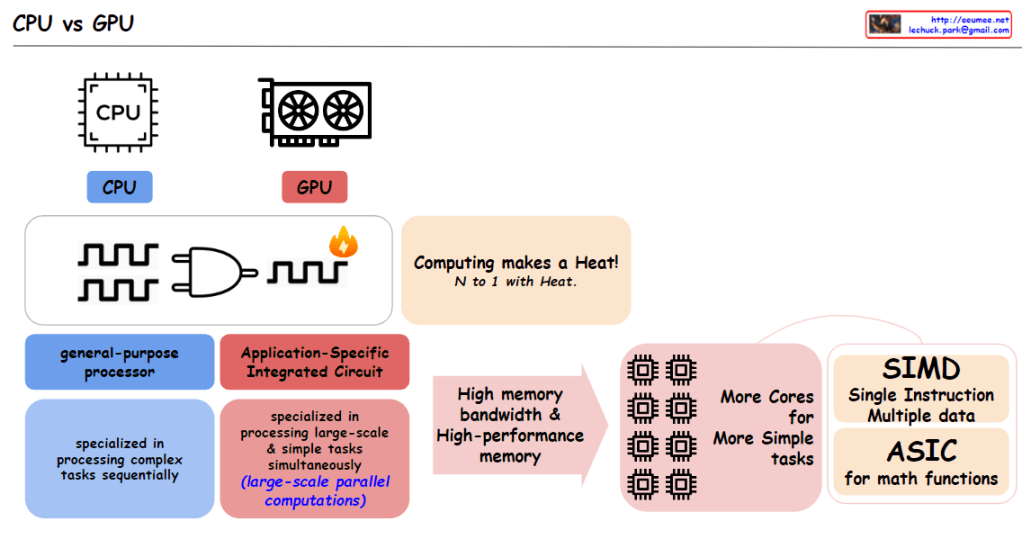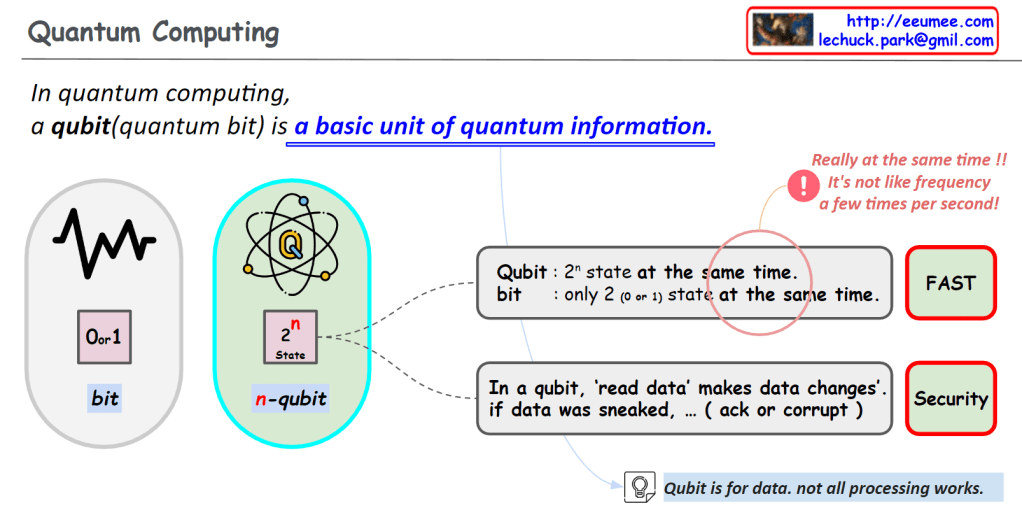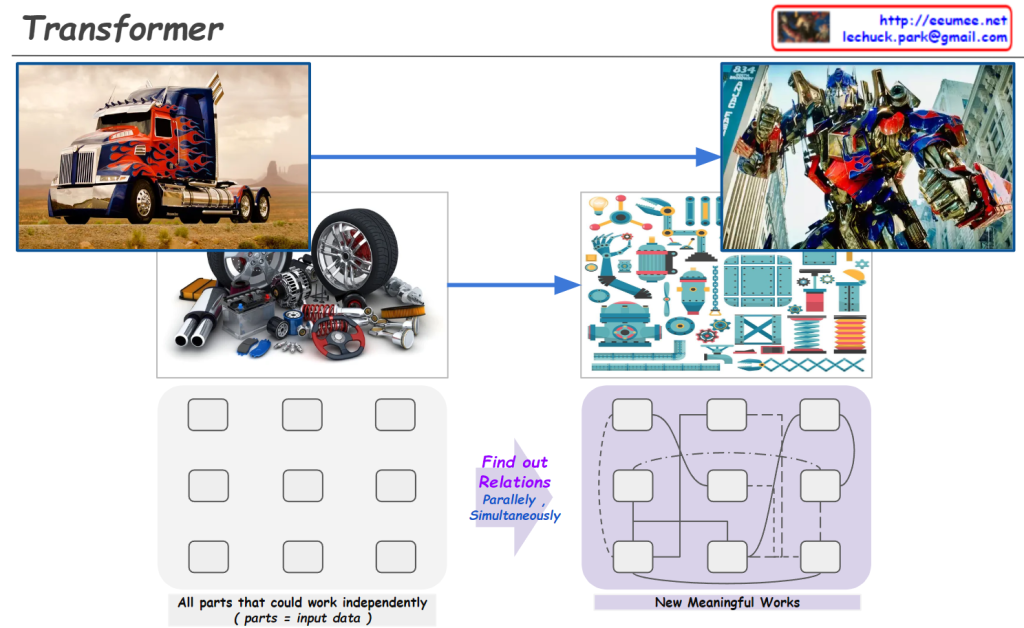
From Claude with some prompting
The image is using an analogy of transforming vehicles to explain the concept of the Transformer architecture in AI language models like myself.
Just like how a vehicle can transform into a robot by having its individual components work in parallel, a Transformer model breaks down the input data (e.g. text) into individual elements (tokens/words). These elements then go through a series of self-attention and feed-forward layers, processing the relationships between all elements simultaneously and in parallel.
This allows the model to capture long-range dependencies and derive contextual meanings, eventually transforming the input into a meaningful representation (e.g. understanding text, generating language). The bottom diagram illustrates this parallel and interconnected nature of processing in Transformers.
So in essence, the image draws a clever analogy between transforming vehicles and how Transformer models process and “transform” input data into contextualized representations through its parallelized and self-attentive computations.