From Claude with some prompting
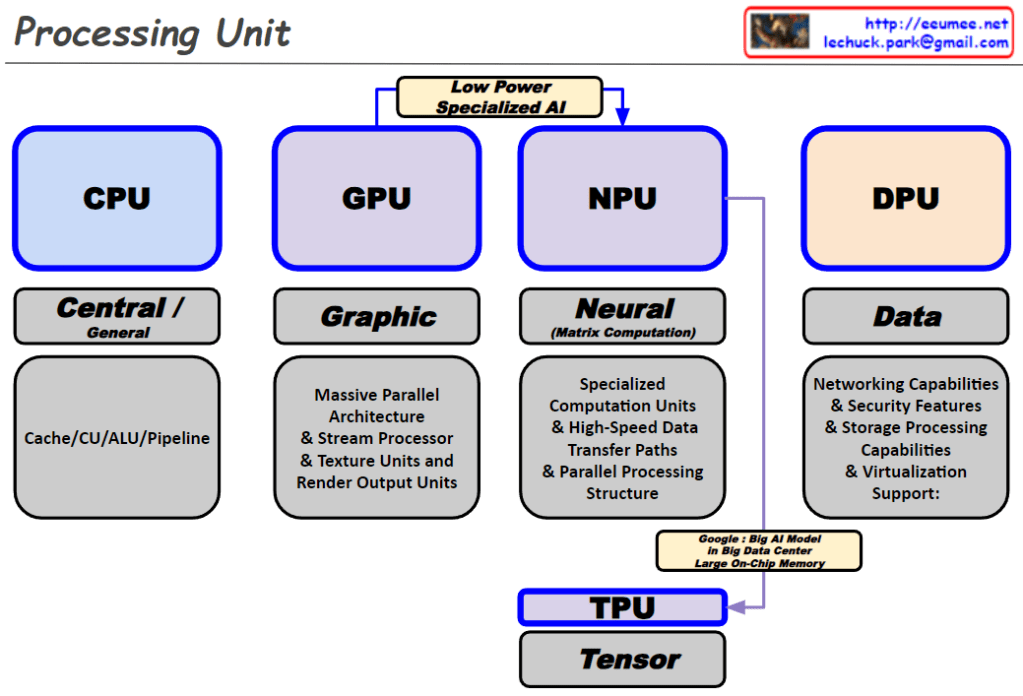
This image illustrates the surge in data and the advancement of AI technologies, particularly parallel processing techniques that efficiently handle massive amounts of data. As a result, there is a growing need for infrastructure technologies that can support such data processing capabilities. Technologies like big data processing, parallel processing, direct memory access, and GPU computing have evolved to meet this demand. The overall flow depicts the data explosion, the advancement of AI and parallel processing techniques, and the evolution of supporting infrastructure technologies.