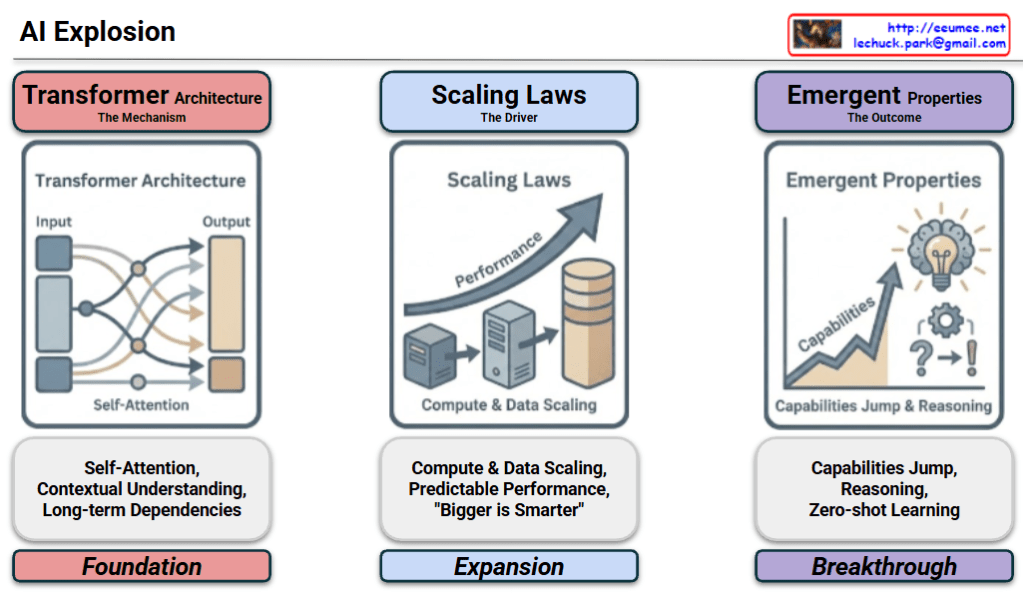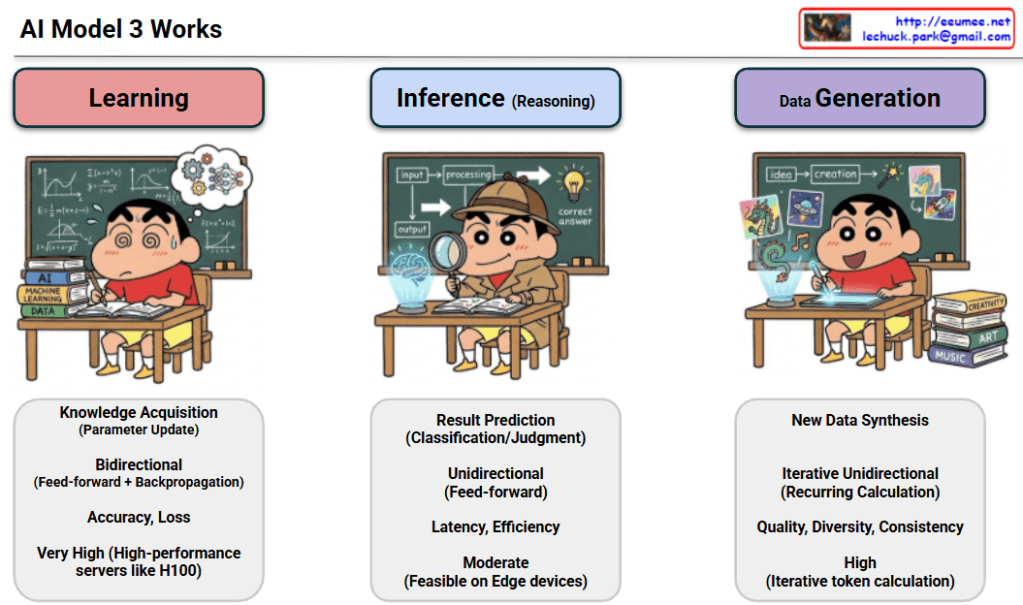
Analysis of AI Model 3 Works
The provided image illustrates the three core stages of how AI models operate: Learning, Inference, and Data Generation.
1. Learning
- Goal: Knowledge acquisition and parameter updates. This is the stage where the AI “studies” data to find patterns.
- Mechanism: Bidirectional (Feed-forward + Backpropagation). It processes data to get a result and then goes backward to correct errors by adjusting internal weights.
- Key Metrics: Accuracy and Loss. The objective is to minimize loss to increase the model’s precision.
- Resource Requirement: Very High. It requires high-performance server clusters equipped with powerful GPUs like the NVIDIA H100.
2. Inference (Reasoning)
- Goal: Result prediction, classification, and judgment. This is using a pre-trained model to answer specific questions (e.g., “What is in this picture?”).
- Mechanism: Unidirectional (Feed-forward). Data simply flows forward through the model to produce an output.
- Key Metrics: Latency and Efficiency. The focus is on how quickly and cheaply the model can provide an answer.
- Resource Requirement: Moderate. It is efficient enough to be feasible on “Edge devices” like smartphones or local PCs.
3. Data Generation
- Goal: New data synthesis. This involves creating entirely new content like text, images, or music (e.g., Generative AI like ChatGPT).
- Mechanism: Iterative Unidirectional (Recurring Calculation). It generates results piece by piece (token by token) in a repetitive process.
- Key Metrics: Quality, Diversity, and Consistency. The focus is on how natural and varied the generated output is.
- Resource Requirement: High. Because it involves iterative calculations for every single token, it requires more power than simple inference.
Summary
- AI processes consist of Learning (studying data), Inference (applying knowledge), and Data Generation (creating new content).
- Learning requires massive server power for bidirectional updates, while Inference is optimized for speed and can run on everyday devices.
- Data Generation synthesizes new information through repetitive, iterative calculations, requiring high resources to maintain quality.
#AI #MachineLearning #GenerativeAI #DeepLearning #TechExplained #AIModel #Inference #DataScience #Learning #DataGeneration
With Gemini