From Claude with some prompting
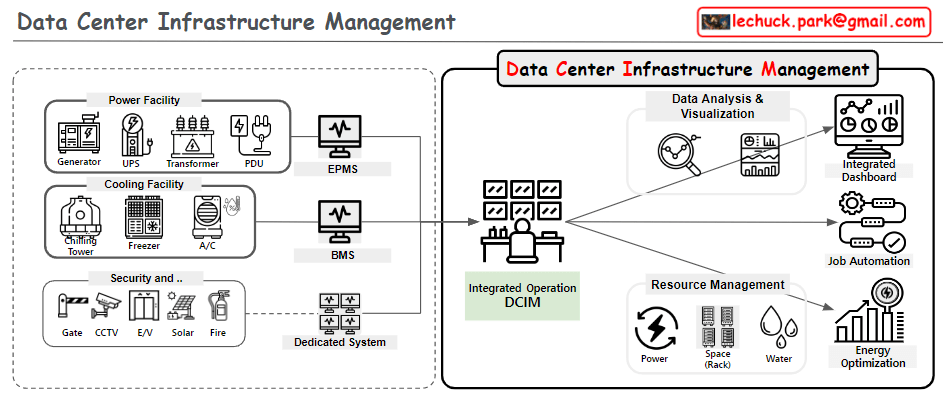
This image illustrates the distinction between BAS (Building Automation System), EPMS (Energy Power Management System), and DCIM (Data Center Infrastructure Management), explaining their development and relationships.
- BAS (Building Automation System):
- Focuses on general buildings
- Emphasizes water management and HVAC (cooling) systems
- Named “BAS” because water and air conditioning were crucial elements in building management
- Primarily deals with low-power usage environments
- Includes water control, cooling control, flow control, and pipe/plumbing management
- EPMS (Energy Power Management System):
- Specialized for high-power usage environments
- Concentrates on power generation, distribution, and control
- Developed separately from BAS due to the unique complexities of high-power environments
- DCIM (Data Center Infrastructure Management):
- Tailored for data center environments
- Integrates functions of both BAS and EPMS
- Manages power (EPMS) and cooling/environmental (BAS) aspects
- Addresses additional requirements specific to data centers
The diagram clearly shows the background and characteristics of each system’s development:
- BAS evolved from the need to manage water and air conditioning in general buildings
- EPMS developed separately due to the specific requirements of high-power environments
- DCIM integrates and expands on BAS and EPMS functionalities to meet the complex needs of data centers
The formula “BAS + EPMS + @ = DCIM” indicates that DCIM incorporates the functions of BAS and EPMS, while also including additional management capabilities (@) specific to data centers.
This structure effectively demonstrates how each system has specialized and evolved to suit particular environments and requirements, and how they are ultimately integrated in DCIM for comprehensive management of data center infrastructures.