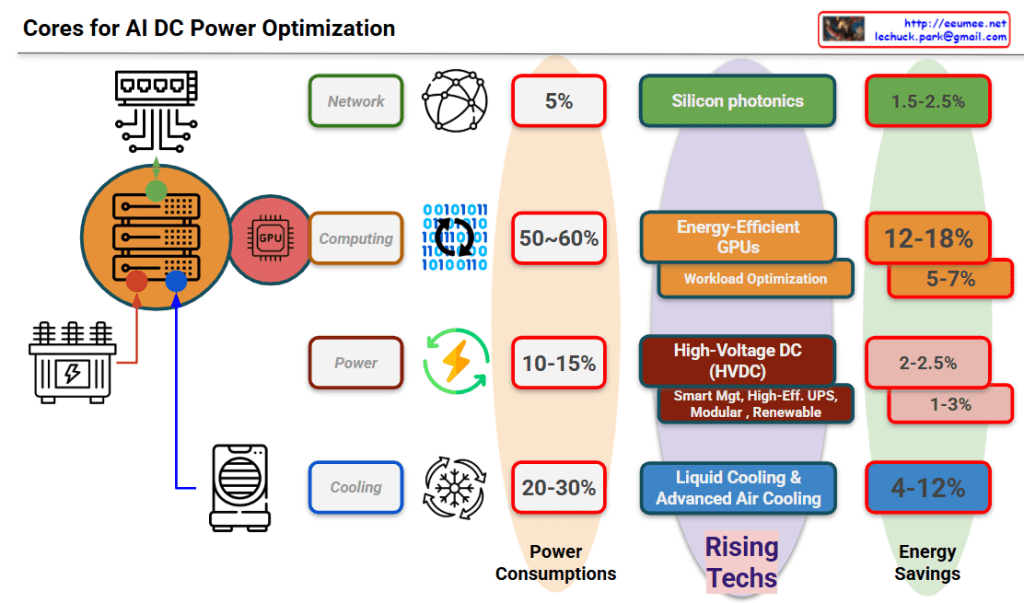
Core Technologies for AI DC Power Optimization
This diagram systematically illustrates the core technologies for AI datacenter power optimization, showing power consumption breakdown by category and energy savings potential of emerging technologies.
Power Consumption Distribution:
- Network: 5% – Data transmission and communication infrastructure
- Computing: 50-60% – GPUs and server processing units (highest consumption sector)
- Power: 10-15% – UPS, power conversion and distribution systems
- Cooling: 20-30% – Server and equipment temperature management systems
Energy Savings by Rising Technologies:
- Silicon Photonics: 1.5-2.5% – Optical communication technology improving network power efficiency
- Energy-Efficient GPUs & Workload Optimization: 12-18% (5-7%) – AI computation optimization
- High-Voltage DC (HVDC): 2-2.5% (1-3%) – Smart management, high-efficiency UPS, modular, renewable energy integration
- Liquid Cooling & Advanced Air Cooling: 4-12% – Cooling system efficiency improvements
This framework presents an integrated approach to maximizing power efficiency in AI datacenters, addressing all major power consumption areas through targeted technological solutions.
With Claude