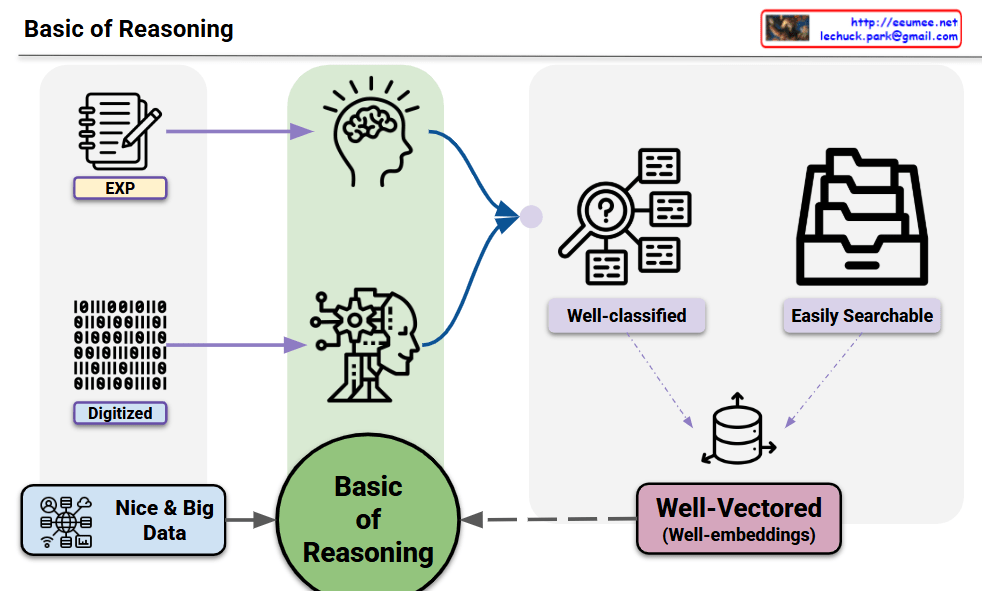
This diagram illustrates that human reasoning and AI reasoning share fundamentally identical structures.
Key Insights:
Common Structure Between Human and AI:
- Human Experience (EXP) = Digitized Data: Human experiential knowledge and AI’s digital data are essentially the same information in different representations
- Both rely on high-quality, large-scale data (Nice & Big Data) as their foundation
Shared Processing Pipeline:
- Both human brain (intuitive thinking) and AI (systematic processing) go through the same Basic of Reasoning process
- Information gets well-classified and structured to be easily searchable
- Finally transformed into well-vectorized embeddings for storage
Essential Components for Reasoning:
- Quality Data: Whether experience or digital information, sufficient and high-quality data is crucial
- Structure: Systematic classification and organization of information
- Vectorization: Conversion into searchable and associative formats
Summary: This diagram demonstrates that effective reasoning – whether human or artificial – requires the same fundamental components: quality data and well-structured, vectorized representations. The core insight is that human experiential learning and AI data processing follow identical patterns, both culminating in structured knowledge storage that enables effective reasoning and retrieval.

