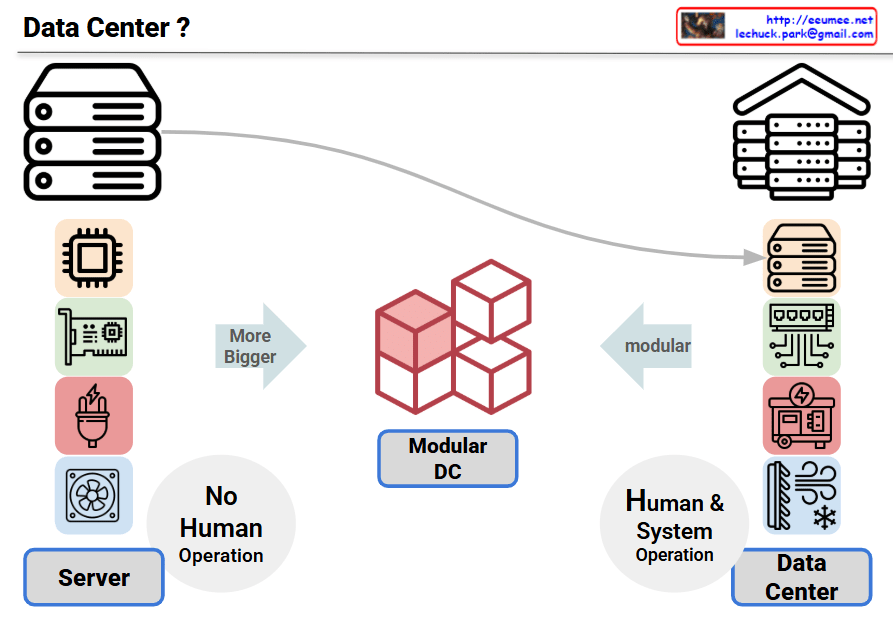
This infographic compares the evolution from servers to data centers, showing the progression of IT infrastructure complexity and operational requirements.
Left – Server
- Shows individual hardware components: CPU, motherboard, power supply, cooling fans
- Labeled “No Human Operation,” indicating basic automated functionality
Center – Modular DC
- Represented by red cubes showing modular architecture
- Emphasizes “More Bigger” scale and “modular” design
- Represents an intermediate stage between single servers and full data centers
Right – Data Center
- Displays multiple server racks and various infrastructure components (networking, power, cooling systems)
- Marked as “Human & System Operation,” suggesting more complex management requirements
Additional Perspective on Automation Evolution:
While the image shows data centers requiring human intervention, the actual industry trend points toward increasing automation:
- Advanced Automation: Large-scale data centers increasingly use AI-driven management systems, automated cooling controls, and predictive maintenance to minimize human intervention.
- Lights-Out Operations Goal: Hyperscale data centers from companies like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft ultimately aim for complete automated operations with minimal human presence.
- Paradoxical Development: As scale increases, complexity initially requires more human involvement, but advanced automation eventually enables a return toward unmanned operations.
Summary: This diagram illustrates the current transition from simple automated servers to complex data centers requiring human oversight, but the ultimate industry goal is achieving fully automated “lights-out” data center operations. The evolution shows increasing complexity followed by sophisticated automation that eventually reduces the need for human intervention.
With Claude
