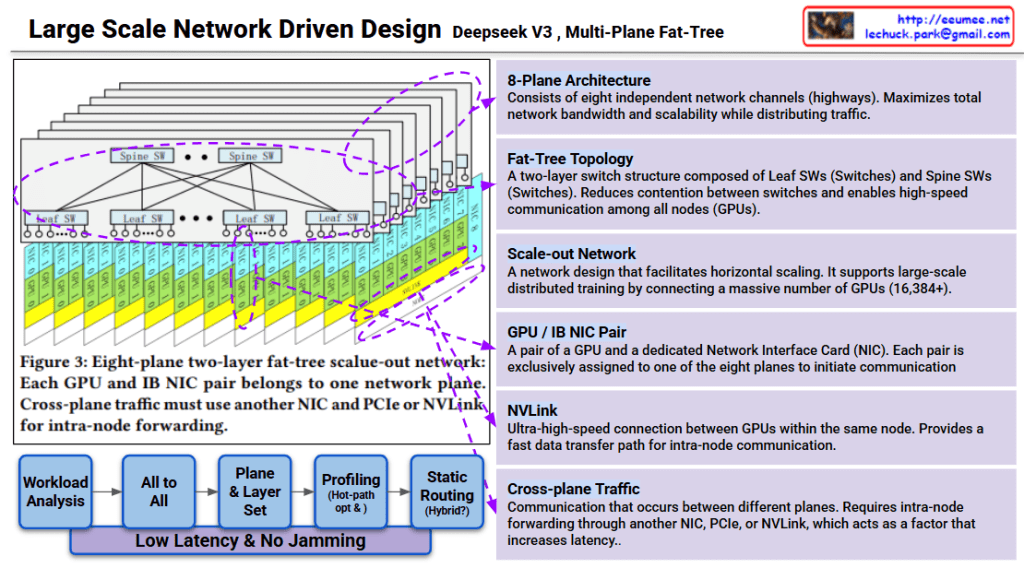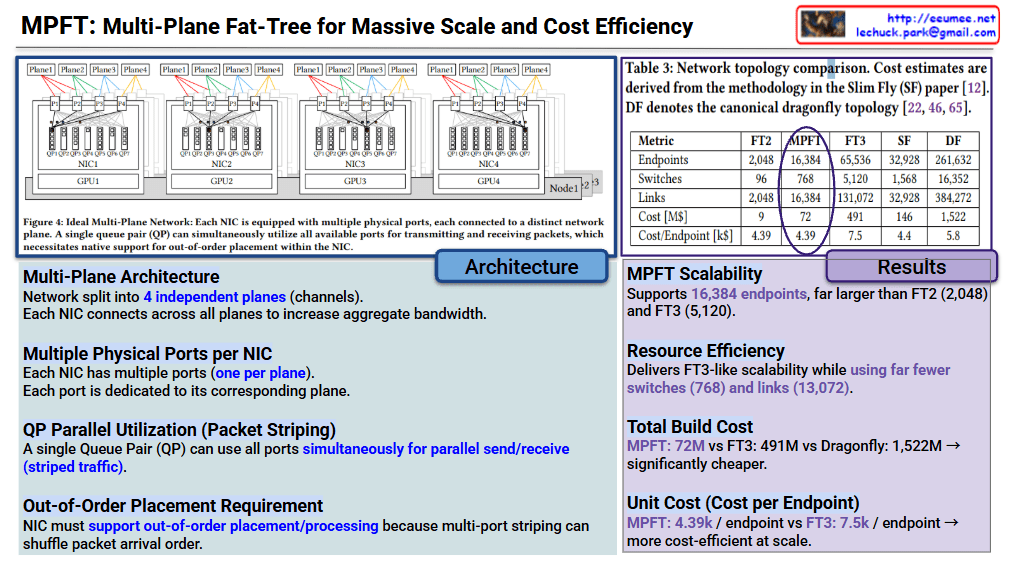
MPFT: Multi-Plane Fat-Tree for Massive Scale and Cost Efficiency
1. Architecture Overview (Blue Section)
The core innovation of MPFT lies in parallelizing network traffic across multiple independent “planes” to maximize bandwidth and minimize hardware overhead.
- Multi-Plane Architecture: The network is split into 4 independent planes (channels).
- Multiple Physical Ports per NIC: Each Network Interface Card (NIC) is equipped with multiple ports—one for each plane.
- QP Parallel Utilization (Packet Striping): A single Queue Pair (QP) can utilize all available ports simultaneously. This allows for striped traffic, where data is spread across all paths at once.
- Out-of-Order Placement: Because packets travel via different planes, they may arrive in a different order than they were sent. Therefore, the NIC must natively support out-of-order processing to reassemble the data correctly.
2. Performance & Cost Results (Purple Section)
The table compares MPFT against standard topologies like FT2/FT3 (Fat-Tree), SF (Slim Fly), and DF (Dragonfly).
| Metric | MPFT | FT3 | Dragonfly (DF) |
| Endpoints | 16,384 | 65,536 | 261,632 |
| Switches | 768 | 5,120 | 16,352 |
| Total Cost | $72M | $491M | $1,522M |
| Cost per Endpoint | $4.39k | $7.5k | $5.8k |
- Scalability: MPFT supports 16,384 endpoints, which is significantly higher than a standard 2-tier Fat-Tree (FT2).
- Resource Efficiency: It achieves high scalability while using far fewer switches (768) and links compared to the 3-tier Fat-Tree (FT3).
- Economic Advantage: At $4.39k per endpoint, it is one of the most cost-efficient models for large-scale data centers, especially when compared to the $7.5k cost of FT3.
Summary
MPFT is presented as a “sweet spot” solution for AI/HPC clusters. It provides the high-speed performance of complex 3-tier networks but keeps the cost and hardware complexity closer to simpler 2-tier systems by using multi-port NICs and traffic striping.
#NetworkArchitecture #DataCenter #HighPerformanceComputing #GPU #AITraining #MultiPlaneFatTree #MPFT #NetworkingTech #ClusterComputing #CloudInfrastructure