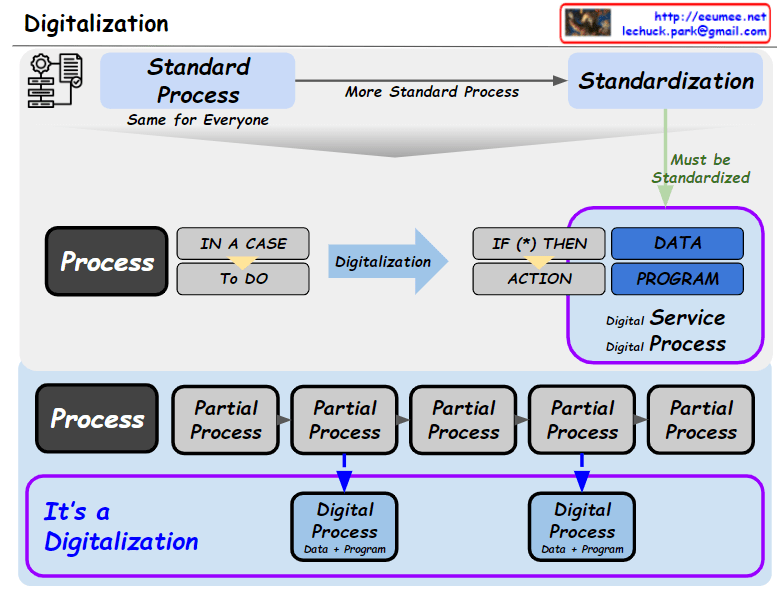
From Claude with some prompting
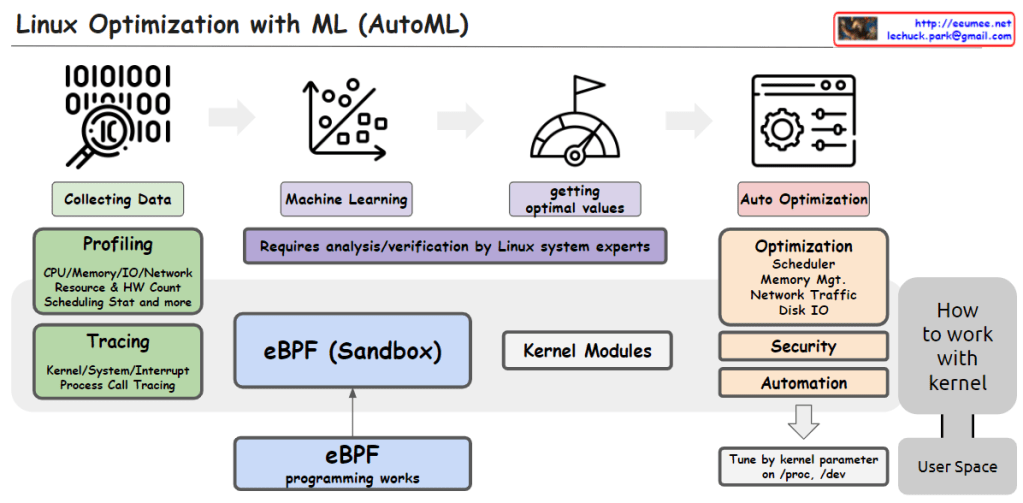
This image illustrates the process of utilizing Machine Learning (ML) and AutoML techniques for system optimization in Linux.
It starts with collecting data through profiling techniques that gather statistics on CPU, memory, I/O, network resource usage, hardware counters, scheduling information, etc. Tracing is also employed to capture kernel/system/interrupt events and process call traces.
The collected data is then used to train machine learning models. This step requires analysis and verification by Linux system experts.
The trained models help determine optimal values, which are then applied to optimize various system components such as the scheduler, memory management, network traffic, and disk I/O. Optimization can also target security and automation aspects.
The eBPF (Enhanced Berkeley Packet Filter) sandbox, situated in the center, allows safe execution within the kernel, enabling eBPF programs to interact with the kernel.
Kernel modules provide another way to implement optimization logic and integrate it directly into the kernel.
Finally, kernel parameters can be tuned from user space to perform optimizations.
In summary, the image depicts an AutoML-based process that leverages data collection, machine learning modeling, deriving optimal values, eBPF, kernel modules, and parameter tuning to automate system optimization in Linux across various kernel subsystems like the scheduler, memory management, network, and disk I/O.C