From DALL-E with some prompting
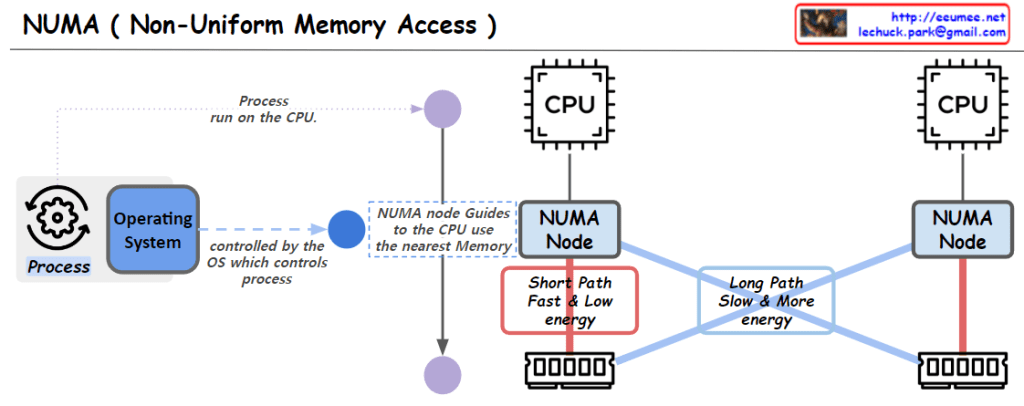
The image depicts the NUMA (Non-Uniform Memory Access) architecture in computer systems. Key elements include:
- Operating System: Manages and controls processes running on the CPU.
- CPU: Central Processing Units where computing tasks are executed.
- NUMA Nodes: Guide CPUs to use the nearest memory, with each NUMA node having memory areas closer to specific CPUs.
- Memory Access Paths: “Short Path” indicates a fast and low-energy memory access that is closer, while “Long Path” represents a slower and more energy-consuming memory access that is farther away.
The structure illustrates that memory access times in a NUMA system are not uniform across all memory, suggesting that memory access optimization can enhance overall system performance.