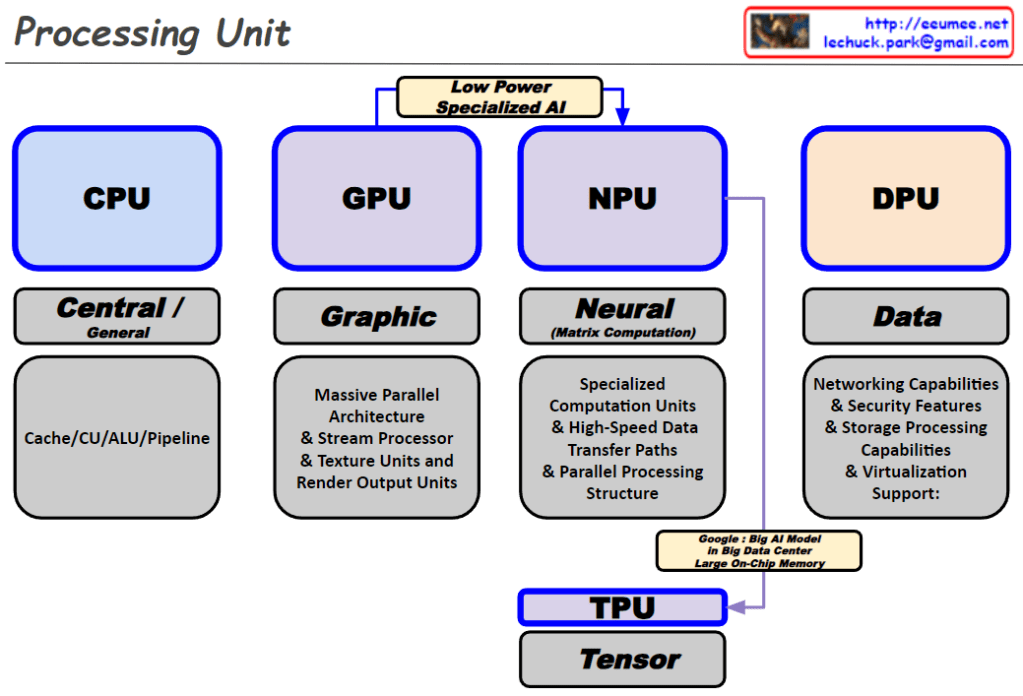
This diagram illustrates the differences between GPU and NPU from a deep learning perspective:
GPU (Graphic Process Unit):
- Originally developed for 3D game rendering
- In deep learning, it’s utilized for parallel processing of vast amounts of data through complex calculations during the training process
- Characterized by “More Computing = Bigger Memory = More Power,” requiring high computing power
- Processes big data and vectorizes information using the “Everything to Vector” approach
- Stores learning results in Vector Databases for future use
NPU (Neuron Process Unit):
- Retrieves information from already trained Vector DBs or foundation models to generate answers to questions
- This process is called “Inference”
- While the training phase processes all data in parallel, the inference phase only searches/infers content related to specific questions to formulate answers
- Performs parallel processing similar to how neurons function
In conclusion, GPUs are responsible for processing enormous amounts of data and storing learning results in vector form, while NPUs specialize in the inference process of generating actual answers to questions based on this stored information. This relationship can be summarized as “training creates and stores vast amounts of data, while inference utilizes this at the point of need.”
With Claude