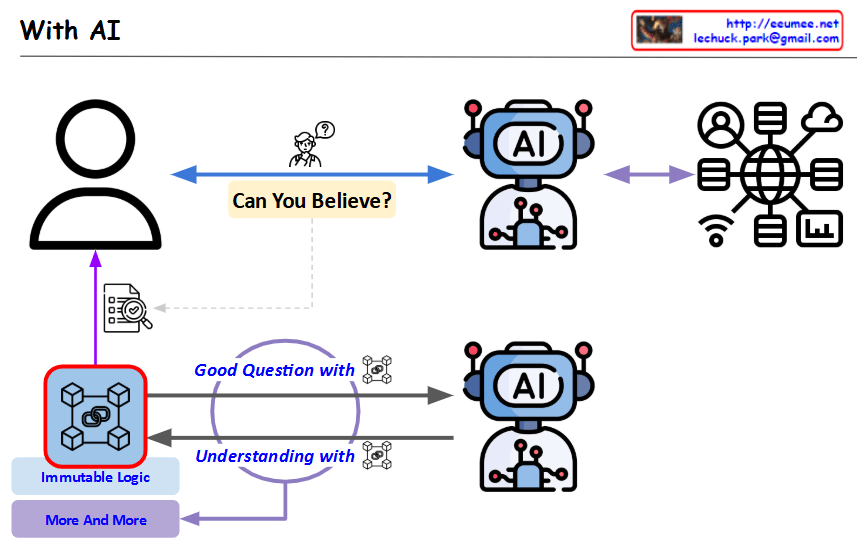
This image illustrates the collaborative problem-solving process between humans and AI through reasoning, emphasizing their complementary relationship rather than a simple comparison.
Key Components and Interpretation
1. AI’s Operational Flow (Upper Section)
- Big Data → Learning → AI Model: The process by which AI builds models through learning from vast amounts of data
- Reasoning → Inferencing → Answer: The process by which AI receives questions and generates answers through reasoning
2. Human Role (Lower Section)
- Experience: Knowledge and information acquired through direct experience
- Logic: A logical thinking framework built upon experience
- Reasoning: The cognitive process that combines experience and logic
3. Critical Interaction Mechanisms
Question:
- Human reasoning results are input to AI in the form of sophisticated questions
- These are not simple queries, but systematic and meaningful questions based on experience and logic
Answer:
- AI’s responses are fed back into the human reasoning process
- Humans verify AI’s answers and integrate them into new experiences and logic for deeper reasoning
4. Core Message
The red-highlighted phrase “humans must possess a strong, experience-based logical framework” represents the diagram’s central theme:
- To collaborate effectively with AI, humans must also possess strong logical thinking frameworks based on experience
- The ability to provide appropriate questions and properly verify and utilize AI’s responses is essential
Conclusion
This image demonstrates that human roles do not disappear in the AI era, but rather become more crucial. Human reasoning abilities based on experience and logic play a pivotal role in AI collaboration, and through this, humans and AI can create synergy for better problem-solving. The diagram presents a collaborative model where both entities work together to achieve superior results.
The key insight is that AI advancement doesn’t replace human thinking but rather requires humans to develop stronger reasoning capabilities to maximize the potential of human-AI collaboration.
With Claude, Gemini