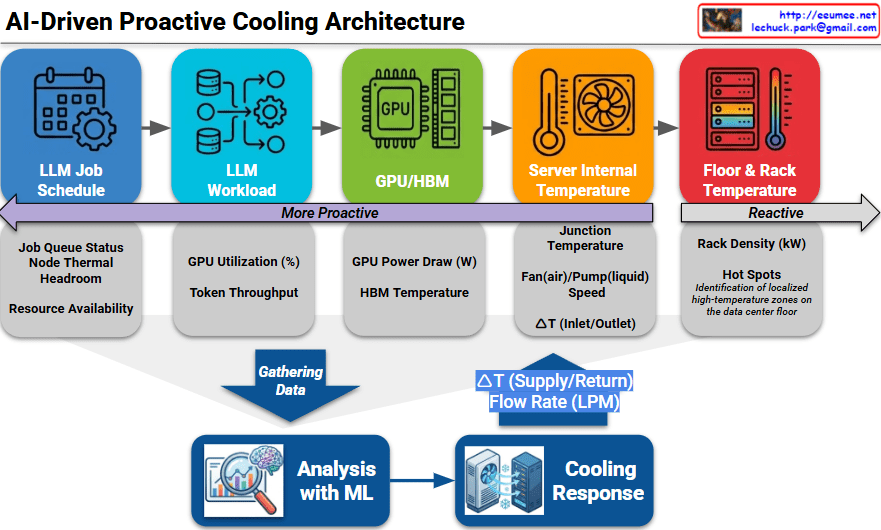
The provided image illustrates an AI-Driven Proactive Cooling Architecture, detailing a sophisticated pipeline that transforms operational data into precise thermal management.
1. The Proactive Data Hierarchy
The architecture categorizes data sources along a spectrum, moving from “More Proactive” (predicting future heat) to “Reactive” (measuring existing heat).
- LLM Job Schedule (Most Proactive): This layer looks at the job queue, node thermal headroom, and resource availability. It allows the system to prepare for heat before the first calculation even begins.
- LLM Workload: Monitors real-time GPU utilization (%) and token throughput to understand the intensity of the current processing task.
- GPU / HBM: Captures direct hardware telemetry, including GPU power draw (Watts) and High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) temperatures.
- Server Internal Temperature: Measures the junction temperature, fan/pump speeds, and the $\Delta T$ (temperature difference) between server inlet and outlet.
- Floor & Rack Temperature (Reactive): The traditional monitoring layer that identifies hot spots and rack density (kW) once heat has already entered the environment.
2. The Analysis and Response Loop
The bottom section of the diagram shows how this multi-layered data is converted into action:
- Gathering Data: Telemetry from all five layers is aggregated into a central repository.
- Analysis with ML: A Machine Learning engine processes this data to predict thermal trends. It doesn’t just look at where the temperature is now, but where it will be in the next few minutes based on the workload.
- Cooling Response: The ML insights trigger physical adjustments in the cooling infrastructure, specifically controlling the $\Delta T$ (Supply/Return) and Flow Rate (LPM – Liters Per Minute) of the coolant.
3. Technical Significance
By shifting the control logic “left” (toward the LLM Job Schedule), data centers can eliminate the thermal lag inherent in traditional systems. This is particularly critical for AI infrastructure, where GPU power consumption can spike almost instantaneously, often faster than traditional mechanical cooling systems can ramp up.
Summary
- This architecture shifts cooling from a reactive sensor-based model to a proactive workload-aware model using AI/ML.
- It integrates data across the entire stack, from high-level LLM job queues down to chip-level GPU power draw and rack temperatures.
- The ML engine predicts thermal demand to dynamically adjust coolant flow rates and supply temperatures, significantly improving energy efficiency and hardware longevity.
#AICooling #DataCenterInfrastructure #ProactiveCooling #GPUManagement #LiquidCooling #LLMOps #ThermalManagement #EnergyEfficiency #SmartDC
With Gemini