From Claude with some prompting
Here’s the interpretation of the image explaining CDC (Change Data Capture) and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes. The diagram is divided into three main sections:
- Top Section:
- Shows CDC/ETL process from “For Operating” database to “For Analysis” database.
- Middle Section (CDC):
- Illustrates the Change Data Capture process
- Shows how changes C1 through C5 are detected and captured
- Key features:
- Realtime processing
- Sync Duplication
- Efficiency
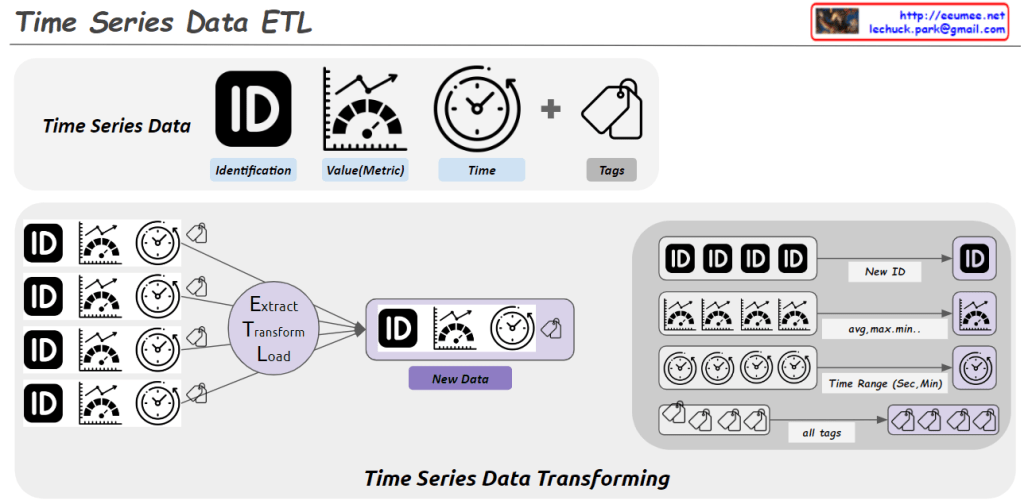
- Bottom Section (ETL):
- Demonstrates traditional ETL process:
- Extract
- Transform
- Load
- Processing characteristics:
- Batch process
- Data Transform
- Data Integrate
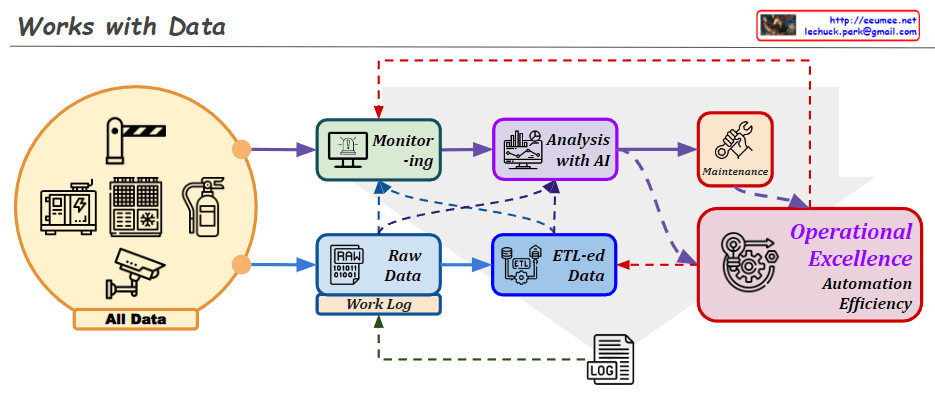
The diagram contrasts two main approaches to data integration:
- CDC: Real-time approach that detects and synchronizes changes as they occur
- ETL: Traditional batch approach that extracts, transforms, and loads data
This visualization effectively shows how CDC provides real-time data synchronization while ETL handles data in batches, each serving different use cases in data integration strategies.