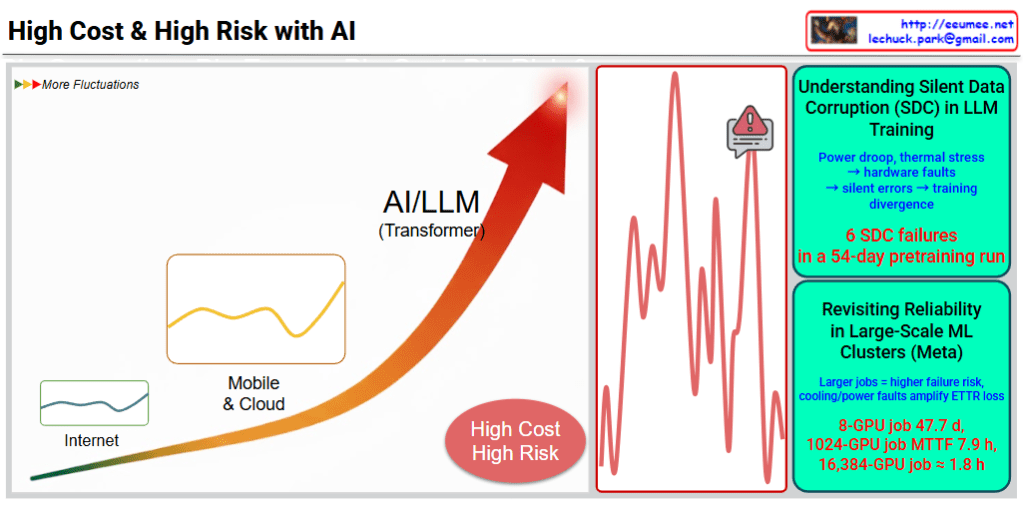
This image illustrates the high cost and high risk of AI/LLM (Large Language Model) training.
Key Analysis
Left: AI/LLM Growth Path
- Evolution from Internet → Mobile & Cloud → AI/LLM (Transformer)
- Each stage shows increasing fluctuations in the graph
- Emphasizes “High Cost, High Risk” message
Center: Real Problem Visualization
The red graph shows dramatic performance spikes that occurred during actual training processes.
Top Right: Silent Data Corruption (SDC) Issues
Silent data corruption from hardware failures:
- Power drops, thermal stress → hardware faults
- Silent errors → training divergence
- 6 SDC failures in a 54-day pretraining run
Bottom Right: Reliability Issues in Large-Scale ML Clusters (Meta Case)
Real failure cases:
- 8-GPU job: average 47.7 days
- 1024-GPU job: MTTF (Mean Time To Failure) 7.9 hours
- 16,384-GPU job: failure in approximately 1.8 hours
Summary
- As GPU scale increases, failure probability rises exponentially, making large-scale AI training extremely costly and technically risky.
- Hardware-induced silent data corruption causes training divergence, with 6 failures recorded in just 54 days of pretraining.
- Meta’s experience shows massive GPU clusters can fail in under 2 hours, highlighting infrastructure reliability as a critical challenge.
#AITraining #LLM #MachineLearning #DataCorruption #GPUCluster #MLOps #AIInfrastructure #HardwareReliability #TransformerModels #HighPerformanceComputing #AIRisk #MLEngineering #DeepLearning