With a Claude’s Help
Core Challenge:
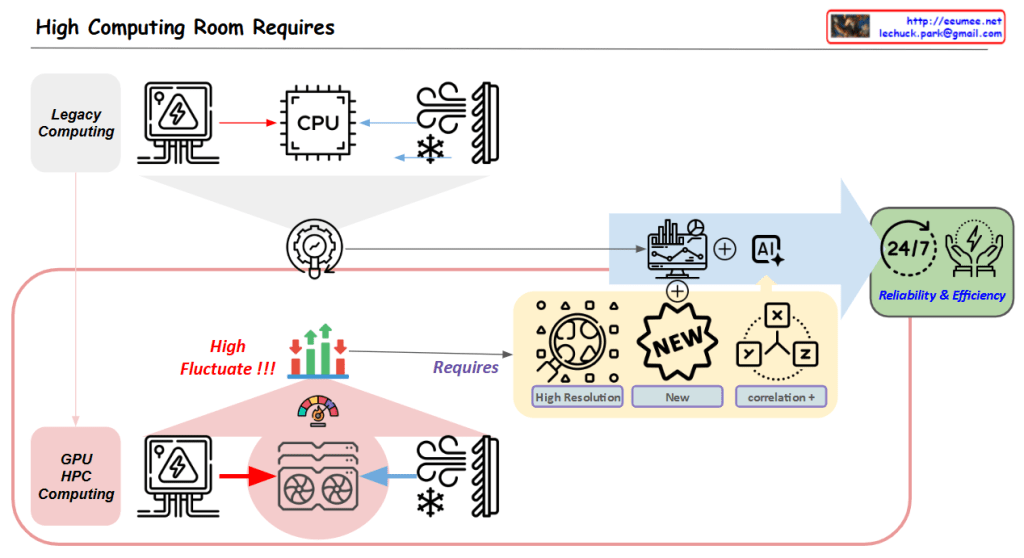
- High Variability in GPU/HPC Computing Room
- Dramatic fluctuations in computing loads
- Significant variations in power consumption
- Changing cooling requirements
Solution Approach:
- Establishing New Data Collection Systems
- High Resolution Data: More granular, time-based data collection
- New Types of Data Acquisition
- Identification of previously overlooked data points
- New Correlation Analysis
- Understanding interactions between computing/power/cooling
- Discovering hidden patterns among variables
- Deriving predictable correlations
Objectives:
- Managing variability through AI-based analysis
- Enhancing system stability
- Improving overall facility operational efficiency
In essence, the diagram emphasizes that to address the high variability challenges in GPU/HPC environments, the key strategy is to collect more precise and new types of data, which enables the discovery of new correlations, ultimately leading to improved stability and efficiency.
This approach specifically targets the inherent variability of GPU/HPC computing rooms by focusing on data collection and analysis as the primary means to achieve better operational outcomes.
