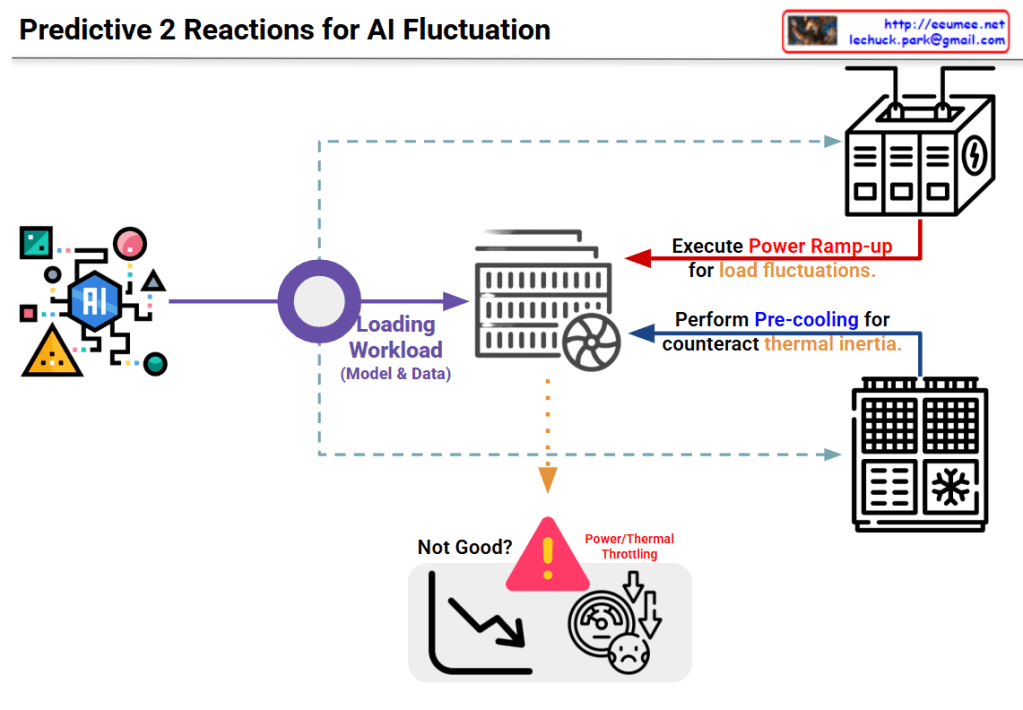
Image Interpretation: Predictive 2-Stage Reactions for AI Fluctuation
This diagram illustrates a two-stage predictive strategy to address load fluctuation issues in AI systems.
System Architecture
Input Stage:
- The AI model on the left generates various workloads (model and data)
Processing Stage:
- Generated workloads are transferred to the central server/computing system
Two-Stage Predictive Reaction Mechanism
Stage 1: Power Ramp-up
- Purpose: Prepare for load fluctuations
- Method: The power supply system at the top proactively increases power in advance
- Preventive measure to secure power before the load increases
Stage 2: Pre-cooling
- Purpose: Counteract thermal inertia
- Method: The cooling system at the bottom performs cooling in advance
- Proactive response to lower system temperature before heat generation
Problem Scenario
The warning area at the bottom center shows problems that occur without these responses:
- Power/Thermal Throttling
- Performance degradation (downward curve in the graph)
- System dissatisfaction state
Key Concept
This system proposes an intelligent infrastructure management approach that predicts rapid fluctuations in AI workloads and proactively adjusts power and cooling before actual loads occur, thereby preventing performance degradation.
Summary
This diagram presents a predictive two-stage reaction system for AI workload management that combines proactive power ramp-up and pre-cooling to prevent thermal throttling. By anticipating load fluctuations before they occur, the system maintains optimal performance without degradation. The approach represents a shift from reactive to predictive infrastructure management in AI computing environments.
#AIInfrastructure #PredictiveComputing #ThermalManagement #PowerManagement #AIWorkload #DataCenterOptimization #ProactiveScaling #AIPerformance #ThermalThrottling #SmartCooling #MLOps #AIEfficiency #ComputeOptimization #InfrastructureAsCode #AIOperations
With Claude
