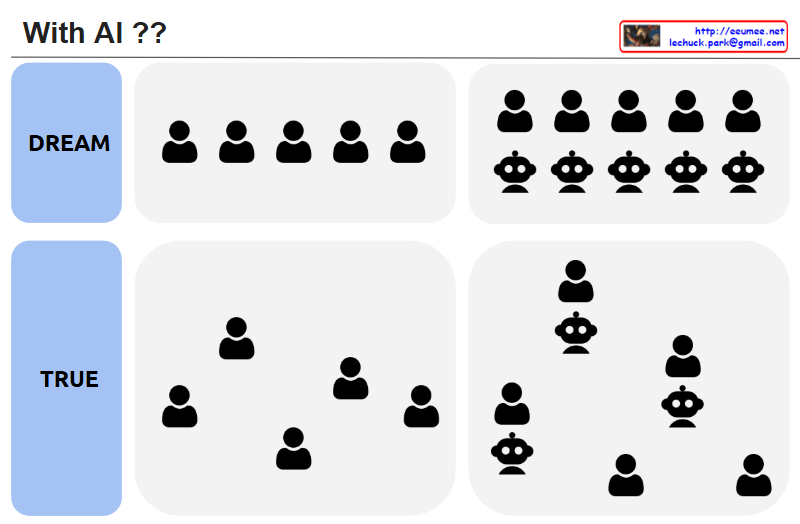
1. Image Structure
The image is divided into “DREAM” (ideal) and “TRUE” (reality), contrasting human society and AI integration scenarios.
2. Human Society Representation
Ideal (DREAM)
- All human icons positioned at the same height
- Symbolizes perfect social equality
- Presents a utopian vision without hierarchical or power differences
Reality (TRUE)
- Human icons placed irregularly at different heights
- Reflects the inevitable existence of social hierarchy and power structures
- Suggests that perfect equality is difficult to achieve in reality
3. AI and Human Relationship
Ideal (DREAM)
- AI icons aligned uniformly below human icons
- Represents AI under complete human control
- Expresses the expectation that humans can perfectly control AI as a tool
Reality (TRUE)
- AI and human icons randomly placed at various heights
- Some AI icons positioned higher than humans
- Indicates that AI may surpass human capabilities or authority in certain domains
4. Key Messages
- Perfect equality in human society remains an ideal, while reality always contains some form of hierarchy.
- The expectation of complete control over AI may be unrealistic, as AI can potentially exceed human capabilities in specific areas.
- It’s important to acknowledge and understand the gap between ideals and reality.
5. Overall Implications
The image effectively visualizes the disconnect between our expectations and reality in both human social structures and AI integration. It suggests that while we may dream of perfect equality and control, the reality is more complex and unpredictable, requiring us to adapt our understanding and expectations accordingly.
With Claude