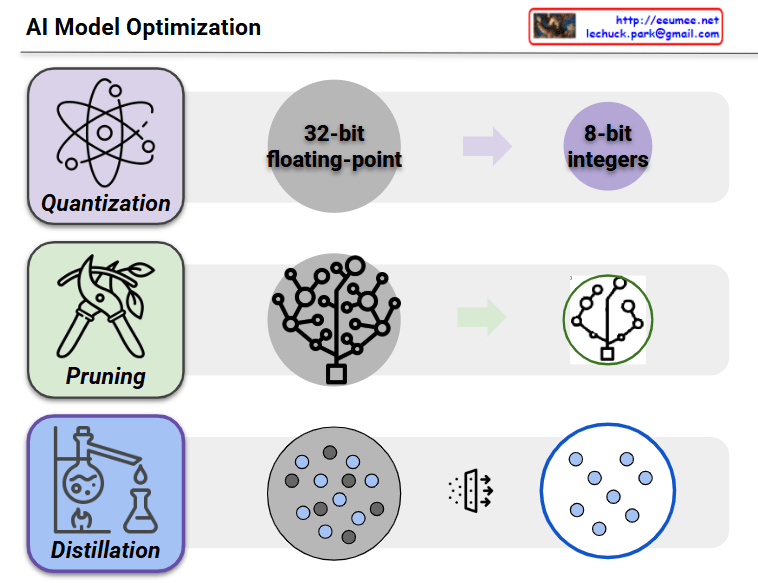
This image shows a diagram illustrating three major AI model optimization techniques.
1. Quantization
- The process of converting 32-bit floating-point numbers to 8-bit integers
- A technique that dramatically reduces model size while maintaining performance
- Significantly decreases memory usage and computational complexity
2. Pruning
- The process of removing less important connections or neurons from neural networks
- Transforms complex network structures into simpler, more efficient forms
- Reduces model size and computation while preserving core functionality
3. Distillation
- A technique that transfers knowledge from a large model (teacher model) to a smaller model (student model)
- Reproduces the performance of complex models in lighter, more efficient models
- Greatly improves efficiency during deployment and execution
All three techniques are essential methods for optimizing AI models to be more efficiently used in real-world environments. They are particularly crucial technologies when deploying AI models in mobile devices or edge computing environments.
With Claude

