The Evolution of AI Computing
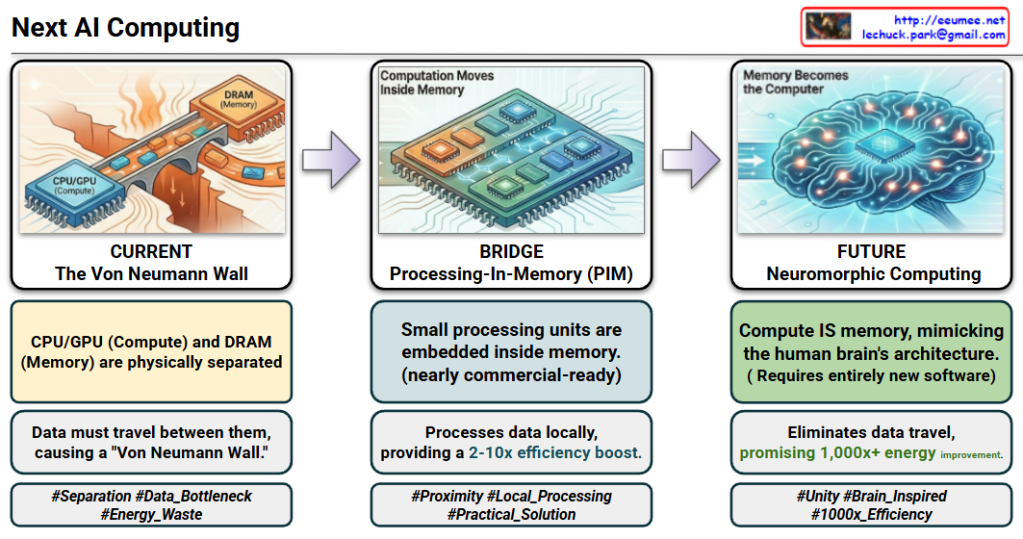
The provided images illustrate the architectural shift in AI computing from the traditional “Separation” model to a “Unified” brain-inspired model, focusing on overcoming energy inefficiency and data bottlenecks.
1. CURRENT: The Von Neumann Wall (Separation)
- Status: The industry standard today.
- Structure: Computation (CPU/GPU) and Memory (DRAM) are physically separate.
- Problem: Constant data movement between components creates a “Von Neumann Wall” (bottleneck).
- Efficiency: Extremely wasteful; 60-80% of energy is consumed just moving data, not processing it.
2. BRIDGE: Processing-In-Memory (PIM) (Proximity)
- Status: Practical, near-term solution; nearly commercial-ready.
- Structure: Small processing units are embedded inside the memory.
- Benefit: Processes data locally to provide a 2-10x efficiency boost.
- Primary Use: Ideal for accelerating Large Language Models (LLMs).
3. FUTURE: Neuromorphic Computing (Unity)
- Status: Future-oriented paradigm shift.
- Structure: Compute IS memory, mimicking the human brain’s architecture where memory elements perform calculations.
- Benefit: Eliminates data travel entirely, promising a massive 1,000x+ energy improvement.
- Requirement: Requires a complete overhaul of current software stacks.
- Primary Use: Ultra-low power Edge devices and Robotics.
#AIComputing #NextGenAI #VonNeumannWall #PIM #ProcessingInMemory #NeuromorphicComputing #EnergyEfficiency #LLM #EdgeAI #Semiconductor #FutureTech #ComputerArchitecture
With Gemini
