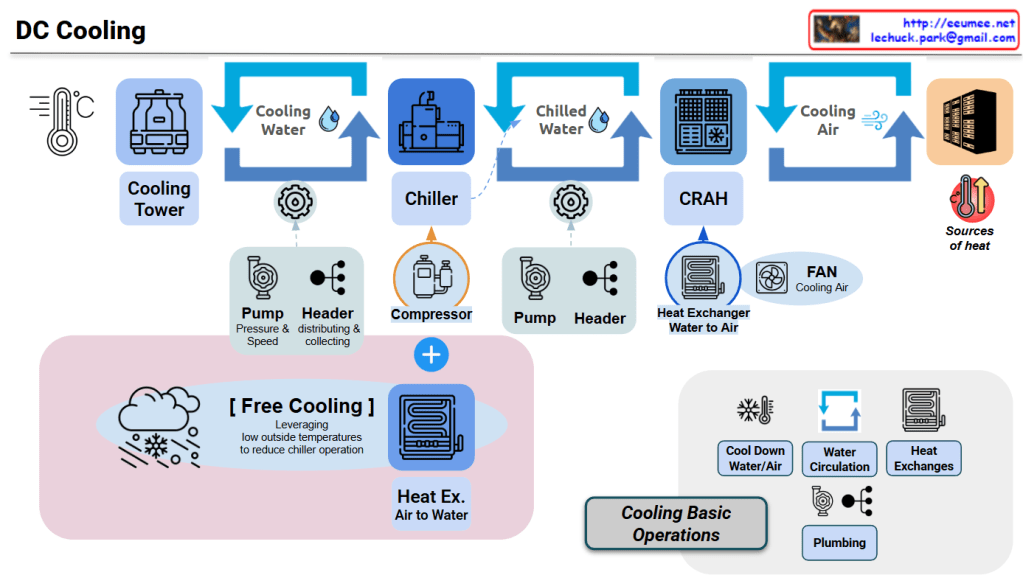
Data Center Cooling System Core Structure
This diagram illustrates an integrated data center cooling system centered on chilled water/cooling water circulation and heat exchange.
Core Cooling Circulation Structure
Primary Loop: Cooling Water Loop
Cooling Tower → Cooling Water → Chiller → (Heat Exchange) → Cooling Tower
- Cooling Tower: Dissipates heat from cooling water to atmosphere using outdoor air
- Pump/Header: Controls cooling water pressure and flow rate through circulation pipes
- Heat Exchange in Chiller: Cooling water exchanges heat with refrigerant to cool the refrigerant
Secondary Loop: Chilled Water Loop
Chiller → Chilled Water → CRAH → (Heat Exchange) → Chiller
- Chiller: Generates chilled water (7-12°C) through compressor and refrigerant cycle
- Pump/Header: Circulates chilled water to CRAH units and returns it back
- Heat Exchange in CRAH: Chilled water exchanges heat with air to cool the air
Tertiary Loop: Cooling Air Loop
CRAH → Cooling Air → Servers → Hot Air → CRAH
- CRAH (Computer Room Air Handler): Generates cooling air through water-to-air heat exchanger
- FAN: Forces circulation of cooling air throughout server room
- Heat Absorption: Air absorbs server heat and returns to CRAH
Heat Exchange Critical Points
Heat Exchange #1: Inside Chiller
- Cooling Water ↔ Refrigerant: Transfers refrigerant heat to cooling water in condenser
- Refrigerant ↔ Chilled Water: Absorbs heat from chilled water to refrigerant in evaporator
Heat Exchange #2: CRAH
- Chilled Water ↔ Air: Transfers air heat to chilled water in water-to-air heat exchanger
- Chilled water temperature rises → Returns to chiller
Heat Exchange #3: Server Room
- Hot Air ↔ Servers: Air absorbs heat from servers
- Temperature-increased air → Returns to CRAH
Energy Efficiency: Free Cooling
Low-Temperature Outdoor Air → Air-to-Water Heat Exchanger → Chilled Water Cooling → Reduced Chiller Load
- Condition: When outdoor temperature is sufficiently low
- Effect: Reduces chiller operation and compressor power consumption (up to 30-50%)
- Method: Utilizes natural cooling through cooling tower or dedicated heat exchanger
Cooling System Control Elements
Cooling Basic Operations Components:
- Cool Down: Controls water/air temperature reduction
- Water Circulation: Adjusts flow rate through pump speed/pressure control
- Heat Exchanges: Optimizes heat exchanger efficiency
- Plumbing: Manages circulation paths and pressure loss
Heat Flow Summary
Server Heat → Air → CRAH (Heat Exchange) → Chilled Water → Chiller (Heat Exchange) →
Cooling Water → Cooling Tower → Atmospheric Discharge
Summary
This system efficiently removes server heat to the outdoor atmosphere through three cascading circulation loops (air → chilled water → cooling water) and three strategic heat exchange points (CRAH, Chiller, Cooling Tower). Free cooling optimization reduces energy consumption by up to 50% when outdoor conditions permit. The integrated pump/header network ensures precise flow control across all loops for maximum cooling efficiency.
#DataCenterCooling #ChilledWater #CRAH #FreeCooling #HeatExchange #CoolingTower #ThermalManagement #DataCenterInfrastructure #EnergyEfficiency #HVACSystem #CoolingLoop #WaterCirculation #ServerCooling #DataCenterDesign #GreenDataCenter
With Claude