Flight LLM (FPGA) Analysis
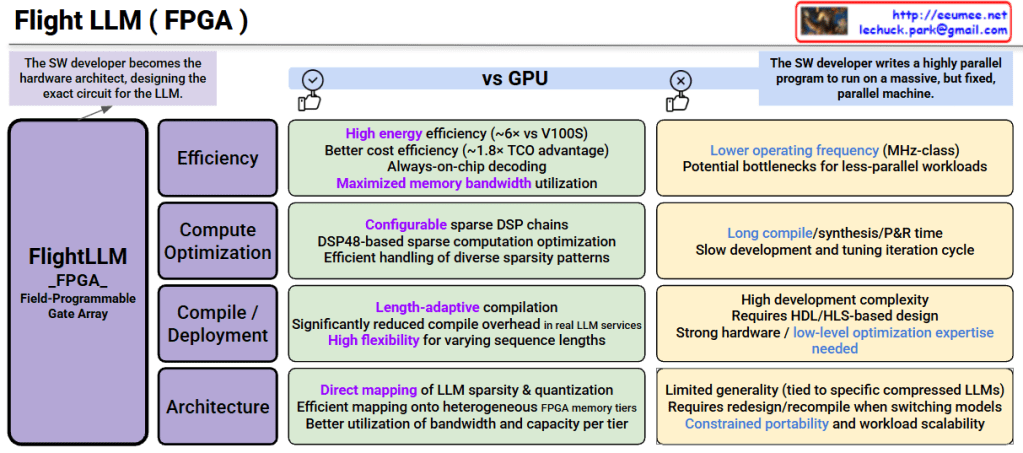
This image is a technical document comparing “FlightLLM,” an FPGA-based LLM (Large Language Model) accelerator, with GPUs.
FlightLLM_FPGA Characteristics
Core Concept: An LLM inference accelerator utilizing Field-Programmable Gate Array, where SW developers become hardware architects, designing the exact circuit for the LLM.
Advantages vs Disadvantages Compared to GPU
✓ FPGA Advantages (Green Boxes)
1. Efficiency
- High energy efficiency (~6x vs V100S)
- Better cost efficiency (~1.8x TCO advantage)
- Always-on-chip decoding
- Maximized memory bandwidth utilization
2. Compute Optimization
- Configurable sparse DSP(Digital Signal Processor) chains
- DSP48-based sparse computation optimization
- Efficient handling of diverse sparsity patterns
3. Compile/Deployment
- Length-adaptive compilation
- Significantly reduced compile overhead in real LLM services
- High flexibility for varying sequence lengths
4. Architecture
- Direct mapping of LLM sparsity & quantization
- Efficient mapping onto heterogeneous FPGA memory tiers
- Better utilization of bandwidth and capacity per tier
✗ FPGA Disadvantages (Orange Boxes)
1. Operating Frequency
- Lower operating frequency (MHz-class)
- Potential bottlenecks for less-parallel workloads
2. Development Time
- Long compile/synthesis/P&R time
- Slow development and iteration cycle
3. Development Complexity
- High development complexity
- Requires HDL/HLS-based design
- Strong hardware/low-level optimization expertise needed
4. Portability Constraints
- Limited generality (tied to specific compressed LLMs)
- Requires redesign/recompile when switching models
- Constrained portability and workload scalability
Key Trade-offs Summary
FPGAs offer superior energy and cost efficiency for specific LLM workloads but require significantly higher development expertise and have lower flexibility compared to GPUs. They excel in massive, fixed parallel workloads but struggle with rapid model iteration and portability.
FlightLLM leverages FPGAs to achieve 6x energy efficiency and 1.8x cost advantage over GPUs through direct hardware mapping of LLM operations. However, this comes at the cost of high development complexity, requiring HDL/HLS expertise and long compilation times. FPGAs are ideal for production deployments of specific LLM models where efficiency outweighs the need for flexibility and rapid iteration.
#FPGA #LLM #AIAccelerator #FlightLLM #HardwareOptimization #EnergyEfficiency #MLInference #CustomHardware #AIChips #DeepLearningHardware
With Claude

