From ChatGPT with some prompting
reflecting the roles of human research and AI/machine learning in the data process:
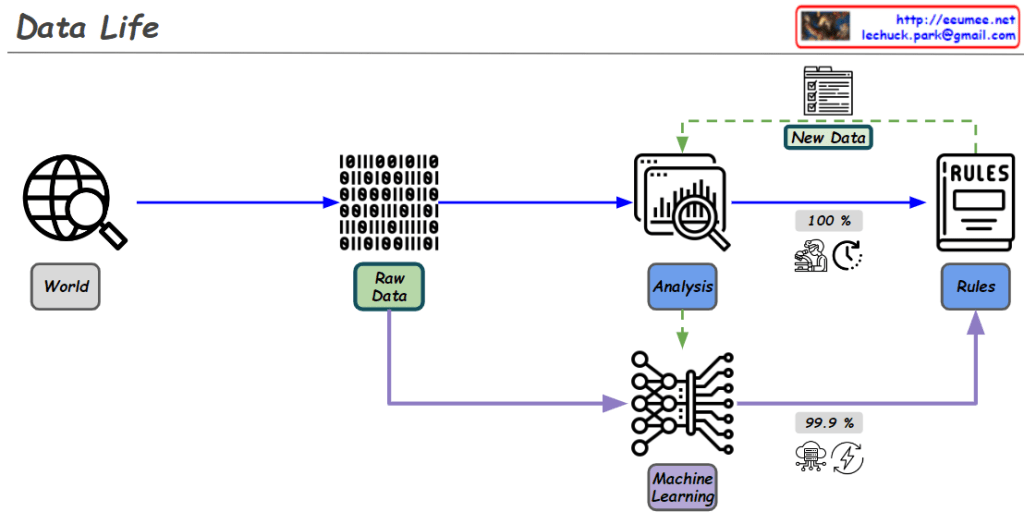
Diagram Explanation :
- World:
- Data is collected from the real world. This could be information from the web, sensor data, or other sources.
- Raw Data:
- The collected data is in its raw, unprocessed form. It is prepared for analysis and processing.
- Analysis:
- The data is analyzed to extract important information and patterns. During this process, rules are created.
- Rules Creation:
- This step is driven by human research.
- The human research process aims for logical and 100% accurate rules.
- These rules are critical for processing and analyzing data with complete accuracy. For example, creating clear criteria for classifying or making decisions based on the data.
- New Data Generation:
- New data is generated during the analysis process, which can be used for further analysis or to update existing rules.
- Machine Learning:
- In this phase, AI models (rules) are trained using the data.
- AI/machine learning goes beyond human-defined rules by utilizing vast amounts of data through computing power to achieve over 99% accuracy in predictions.
- This process relies heavily on computational resources and energy, using probabilistic models to derive results from the data.
- For instance, AI can identify whether an image contains a cat or a dog with over 99% accuracy based on the data it has learned from.
Overall Flow Summary :
- Human research establishes logical rules that are 100% accurate, and these rules are essential for precise data processing and analysis.
- AI/machine learning complements these rules by leveraging massive amounts of data and computing power to find high-probability results. This is done through probabilistic models that continuously improve and refine predictions over time.
- Together, these two approaches enhance the effectiveness and accuracy of data processing and prediction.
This diagram effectively illustrates how human logical research and AI-driven data learning work together in the data processing lifecycle.
