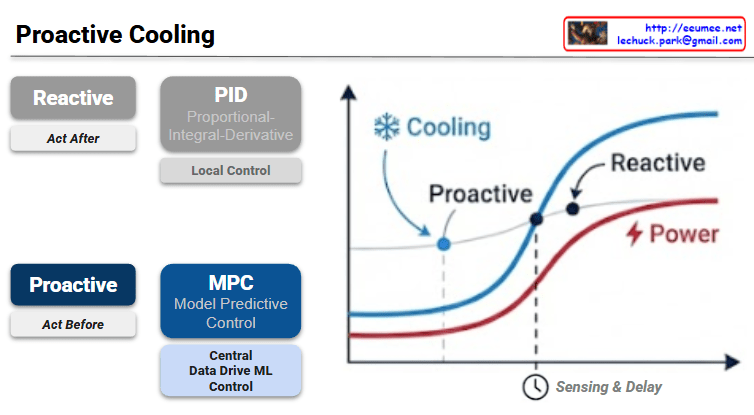
The provided image illustrates the fundamental shift in data center thermal management from traditional Reactive methods to AI-driven Proactive strategies.
1. Comparison of Control Strategies
The slide contrasts two distinct approaches to managing the cooling load in a high-density environment, such as an AI data center.
| Feature | Reactive (Traditional) | Proactive (Advanced) |
| Philosophy | Act After: Responds to changes. | Act Before: Anticipates changes. |
| Mechanism | PID Control: Proportional-Integral-Derivative. | MPC: Model Predictive Control. |
| Scope | Local Control: Focuses on individual units/sensors. | Central ML Control: Data-driven, system-wide optimization. |
| Logic | Feedback-based (error correction). | Feedforward-based (predictive modeling). |
2. Graph Analysis: The “Sensing & Delay” Factor
The graph on the right visualizes the efficiency gap between these two methods:
- Power (Red Line): Represents the IT load or power consumption which generates heat.
- Sensing & Delay: There is a temporal gap between when a server starts consuming power and when the cooling system’s sensors detect the temperature rise and physically ramp up the fans or chilled water flow.
- Reactive Cooling (Dashed Blue Line): Because it “acts after,” the cooling response lags behind the power curve. This often results in thermal overshoot, where the hardware momentarily operates at higher temperatures than desired, potentially triggering throttling.
- Proactive Cooling (Solid Blue Line): By using Model Predictive Control (MPC), the system predicts the impending power spike. It initiates cooling before the heat is fully sensed, aligning the cooling curve more closely with the power curve to maintain a steady temperature.
3. Technical Implications for AI Infrastructure
In modern data centers, especially those handling fluctuating AI workloads (like LLM training or high-concurrency inference), the “Sensing & Delay” in traditional PID systems can lead to significant energy waste and hardware stress. MPC leverages historical data and real-time telemetry to:
- Reduce PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness): By avoiding over-cooling and sudden spikes in fan power.
- Improve Reliability: By maintaining a constant thermal envelope, reducing mechanical stress on chips.
- Optimize Operational Costs: Through centralized, intelligent resource allocation.
Summary
- Proactive Cooling utilizes Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Machine Learning to anticipate heat loads before they occur.
- Unlike traditional PID systems that respond to temperature errors, MPC eliminates the Sensing & Delay lag by acting on predicted power spikes.
- This shift enables superior energy efficiency and thermal stability, which is critical for high-density AI data center operations.
#DataCenter #AICooling #ModelPredictiveControl #MPC #ThermalManagement #EnergyEfficiency #SmartInfrastructure #PUEOptimization #MachineLearning
With Gemini