Multi-Plane Network Topology for Scalable AI Clusters
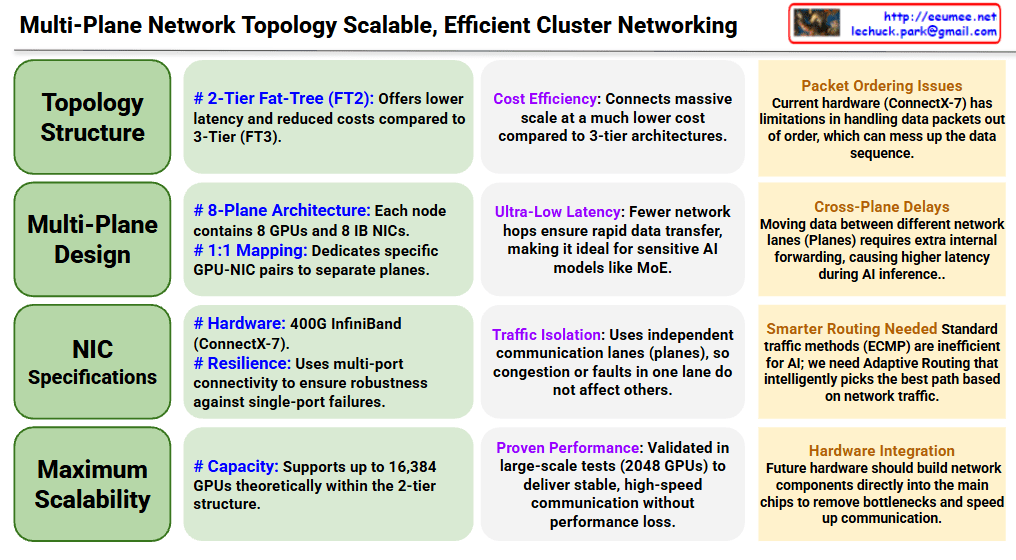
Core Architecture (Left – Green Sections)
Topology Structure
- Adopts 2-Tier Fat-Tree (FT2) architecture for reduced latency and cost efficiency compared to 3-Tier
- Achieves massive scale connections at much lower cost than 3-tier architectures
Multi-Plane Design
- 8-Plane Architecture: Each node contains 8 GPUs and 8 IB NICs
- 1:1 Mapping: Dedicates specific GPU-NIC pairs to separate planes
NIC Specifications
- Hardware: 400G InfiniBand (ConnectX-7)
- Resilience: Multi-port connectivity ensures robustness against single-port failures
Maximum Scalability
- Theoretically supports up to 16,384 GPUs within the 2-tier structure
Advantages (Center – Purple Sections)
Cost Efficiency: Connects massive scale at much lower cost compared to 3-tier architectures
Ultra-Low Latency: Fewer network hops ensure rapid data transfer, ideal for latency-sensitive AI models like MoE
Traffic Isolation: Independent communication lanes (planes) prevent congestion or faults in one lane from affecting others
Proven Performance: Validated in large-scale tests with 2048 GPUs, delivering stable and high-speed communication
Challenges (Right – Orange Sections)
Packet Ordering Issues: Current hardware (ConnectX-7) has limitations in handling out-of-order data packets
Cross-Plane Delays: Moving data between different network planes requires extra internal forwarding, causing higher latency during AI inference
Smarter Routing Needed: Standard traffic methods (ECMP) are inefficient for AI; requires Adaptive Routing that intelligently selects the best path based on network traffic
Hardware Integration: Future hardware should build network components directly into main chips to remove bottlenecks and speed up communication
Summary
This document presents a multi-plane network topology using 2-tier Fat-Tree architecture that scales AI clusters up to 16,384 GPUs cost-effectively with ultra-low latency. The 8-plane design with 1:1 GPU-NIC mapping provides traffic isolation and resilience, though challenges remain in packet ordering and cross-plane communication. Future improvements require smarter routing algorithms and deeper hardware-network integration to optimize AI workload performance.
#AIInfrastructure #DataCenterNetworking #HPC #InfiniBand #GPUCluster #NetworkTopology #FatTree #ScalableComputing #MLOps #AIHardware #DistributedComputing #CloudInfrastructure #NetworkArchitecture #DeepLearning #AIatScale