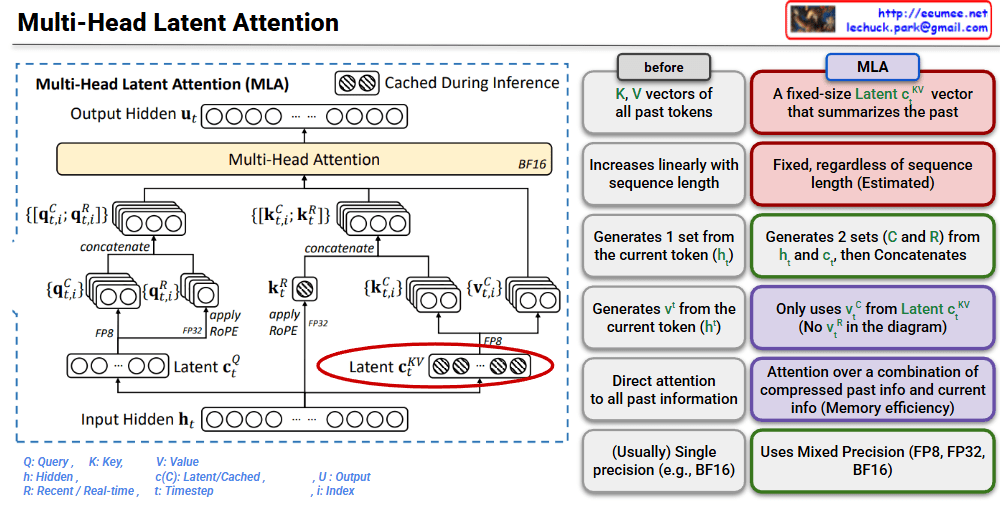
Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA) Interpretation
This image is a technical diagram explaining the structure of Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA).
🎯 Core Concept
MLA is a mechanism that improves the memory efficiency of traditional Multi-Head Attention.
Traditional Approach (Before) vs MLA
Traditional Approach:
- Stores K, V vectors of all past tokens
- Memory usage increases linearly with sequence length
MLA:
- Summarizes past information with a fixed-size Latent vector (c^KV)
- Maintains constant memory usage regardless of sequence length
📊 Architecture Explanation
1. Input Processing
- Starts from Input Hidden State (h_t)
2. Latent Vector Generation
- Latent c_t^Q: For Query of current token (compressed representation)
- Latent c_t^KV: For Key-Value (cached and reused)
3. Query, Key, Value Generation
- Query (q): Generated from current token (h_t)
- Key-Value: Generated from Latent c_t^KV
- Creates Compressed (C) and Recent (R) versions from c_t^KV
- Concatenates both for use
4. Multi-Head Attention Execution
- Performs attention computation with generated Q, K, V
- Uses BF16 (Mixed Precision)
✅ Key Advantages
- Memory Efficiency: Compresses past information into fixed-size vectors
- Faster Inference: Reuses cached Latent vectors
- Information Preservation: Maintains performance by combining compressed and recent information
- Mixed Precision Support: Utilizes FP8, FP32, BF16
🔑 Key Differences
- v_t^R from Latent c_t^KV is not used (purple box on the right side of diagram)
- Value of current token is directly generated from h_t
- This enables efficient combination of compressed past information and current information
This architecture is an innovative approach to solve the KV cache memory problem during LLM inference.
Summary
MLA replaces the linearly growing KV cache with fixed-size latent vectors, dramatically reducing memory consumption during inference. It combines compressed past information with current token data through an efficient attention mechanism. This innovation enables faster and more memory-efficient LLM inference while maintaining model performance.
#MultiHeadLatentAttention #MLA #TransformerOptimization #LLMInference #KVCache #MemoryEfficiency #AttentionMechanism #DeepLearning #NeuralNetworks #AIArchitecture #ModelCompression #EfficientAI #MachineLearning #NLP #LargeLanguageModels
With Claude