With a Claude
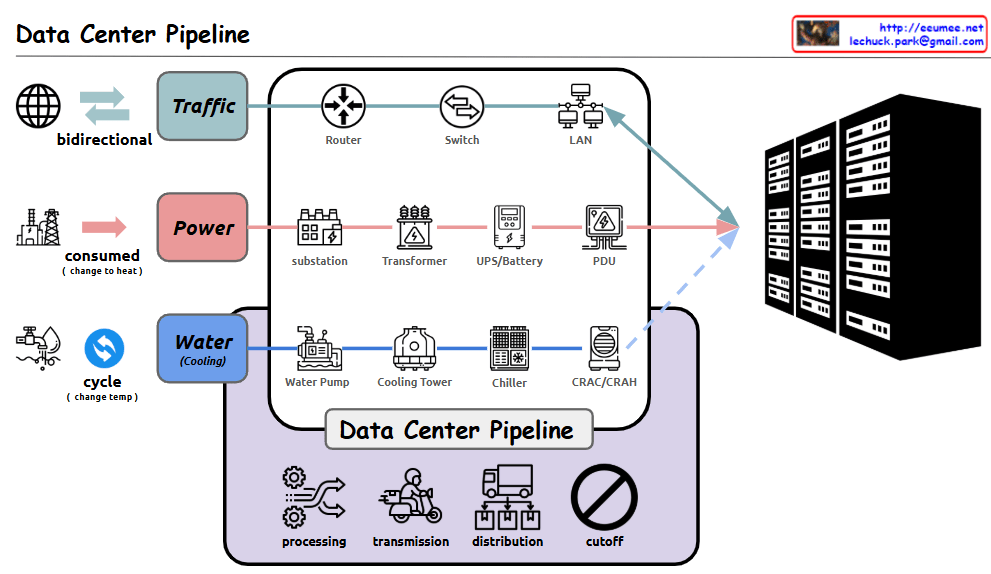
Detailed analysis of the Data Center Pipeline diagram:
- Traffic Pipeline
- Bidirectional network traffic handling
- Infrastructure flow: Router → Switch → LAN
- Responsible for stable data transmission and reception
- Power Pipeline
- Power consumption converted to heat
- Flow: Substation → Transformer → UPS/Battery → PDU (Power Distribution Unit)
- Ensures stable power supply and backup systems
- Water (Cooling) Pipeline
- Circulation cooling system through temperature change
- Flow: Water Pump → Cooling Tower → Chiller → CRAC/CRAH (Computer Room Air Conditioning/Handler)
- Efficiently controls server heat generation
- Data Center Management Functions
- Processing: Data and system processing
- Transmission: Data transfer
- Distribution: Resource allocation
- Cutoff: System protection during emergencies
Comprehensive Summary: This diagram illustrates the core infrastructure of a modern data center. It shows the seamless integration of three critical pipelines: network traffic for data processing, power supply for system operation, and cooling systems for equipment protection. Each pipeline undergoes multiple processing stages, working harmoniously to ensure stable data center operations. The four core management functions – processing, transmission, distribution, and cutoff – guarantee the efficiency and stability of the entire system. This integrated infrastructure design enables reliable operation of data centers, which form the foundation of modern digital services. The careful balance between these systems is crucial for maintaining optimal performance, ensuring business continuity, and protecting valuable computing resources. The design demonstrates how modern data centers handle the complex requirements of digital infrastructure while maintaining reliability and efficiency.