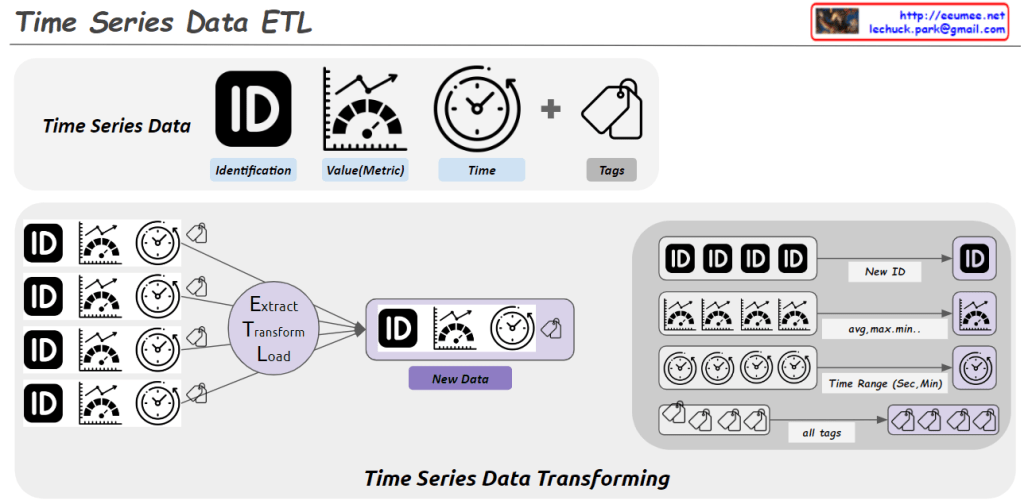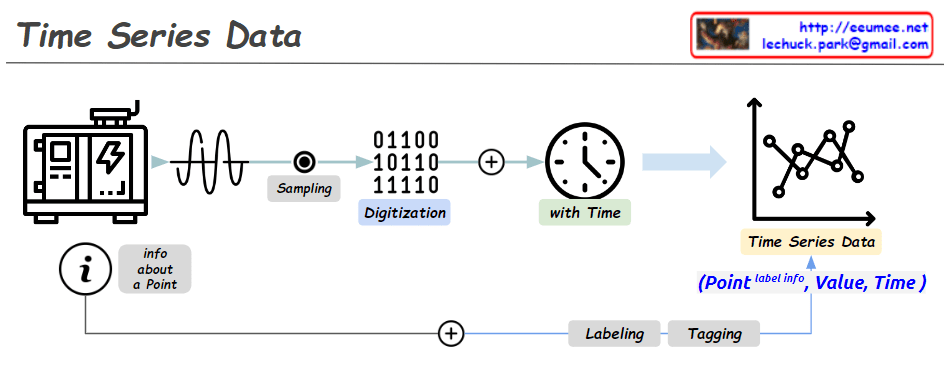
From Claude with some prompting
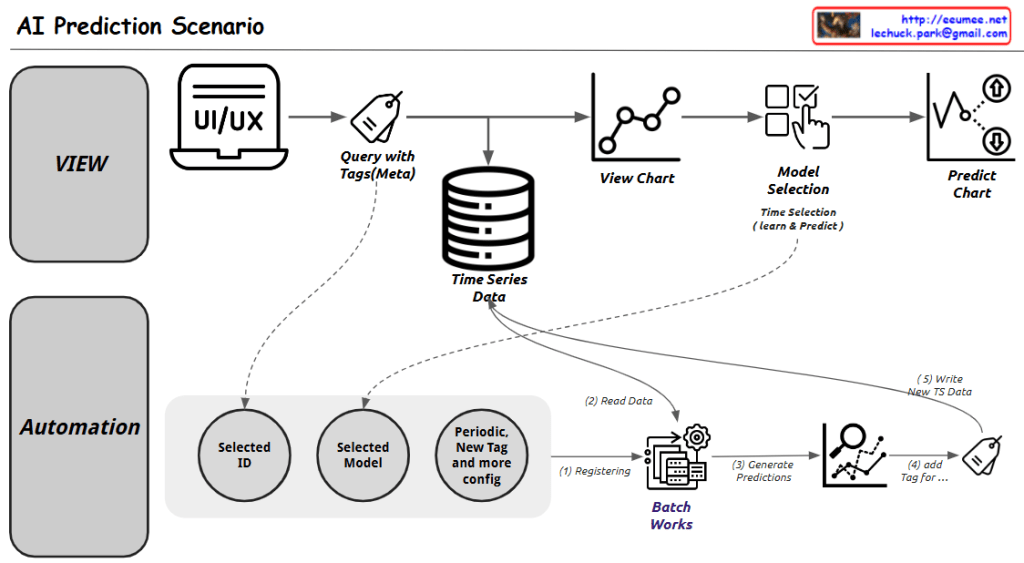
This diagram illustrates an AI Prediction System workflow, which is divided into two main sections:
- Upper Section (VIEW):
- Starts with a UI/UX interface
- Executes queries with tags (metadata)
- Connects to time series data storage
- Displays data visualization charts
- Includes model selection step
- Finally generates prediction charts
- Lower Section (Automation):
- Selected ID
- Selected Model
- Periodic, new tags and additional configuration
- Batch work processing (consisting of 4 steps):
- Registering
- Read Data
- Generate Predictions
- Add Tag
- Writing new time series data
The system provides two main functionalities:
- A user interface for direct data viewing and prediction execution
- Automated batch processing for periodic predictions and data updates
Key Components:
- Time Series Data storage as a central database
- View Chart for data visualization
- Model Selection with time selection (learn & predict)
- Predict Chart as the final output
- Batch Works system for automated processing
The workflow demonstrates a comprehensive approach to handling both manual and automated AI predictions, combining user interaction with systematic data processing and analysis. The system appears designed to handle time series data efficiently while providing both immediate and scheduled prediction capabilities.