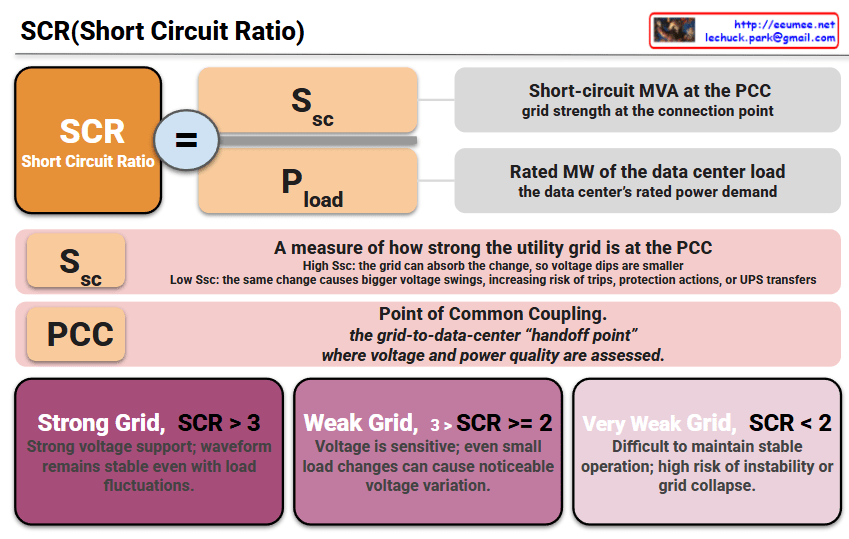
This image is an infographic that explains SCR (Short Circuit Ratio) and why it matters for AI/data center power stability. The main idea is: SCR compares grid strength at the connection point (PCC) against the data center’s load size—lower SCR means more voltage instability.
1) Top: SCR formula
- SCR = Ssc / Pload
- Ssc: Short-circuit MVA at the PCC
→ the grid’s strength / stiffness at the point where the data center connects - Pload: Rated MW of the data center load
→ the data center’s rated power demand
- Ssc: Short-circuit MVA at the PCC
2) Middle: What high vs. low Ssc means (data center impact)
- High Ssc (strong grid)
→ the grid can absorb sudden load changes, so voltage dips are smaller and operation is more stable. - Low Ssc (weak grid)
→ the same load change causes larger voltage swings, increasing the risk of trips, protection actions, or UPS transfers.
3) PCC definition (center-lower)
- PCC (Point of Common Coupling)
→ the grid-to-data-center “handoff point” where voltage and power quality are assessed.
4) Bottom: Grid categories by SCR
- Strong Grid: SCR > 3
→ strong voltage support; waveform remains stable even with load fluctuations. - Weak Grid: 2 ≤ SCR < 3 (shown as 3 > SCR ≥ 2 in the image)
→ voltage is sensitive; small load changes can cause noticeable voltage variation. - Very Weak Grid: SCR < 2
→ difficult to maintain stable operation; high risk of instability or (in extreme cases) grid collapse.
summary
- SCR = grid strength at PCC (Ssc) ÷ data center load (Pload).
- Higher SCR means smaller voltage dips and more stable operation.
- Lower SCR increases power-quality risk (voltage swings, trips, UPS transfers).
#SCR #ShortCircuitRatio #PCC #GridStrength #PowerQuality #DataCenter #AIDatacenter #VoltageStability #BESS #GridForming #SynchronousCondenser #IBR
With ChatGPT