With Claude
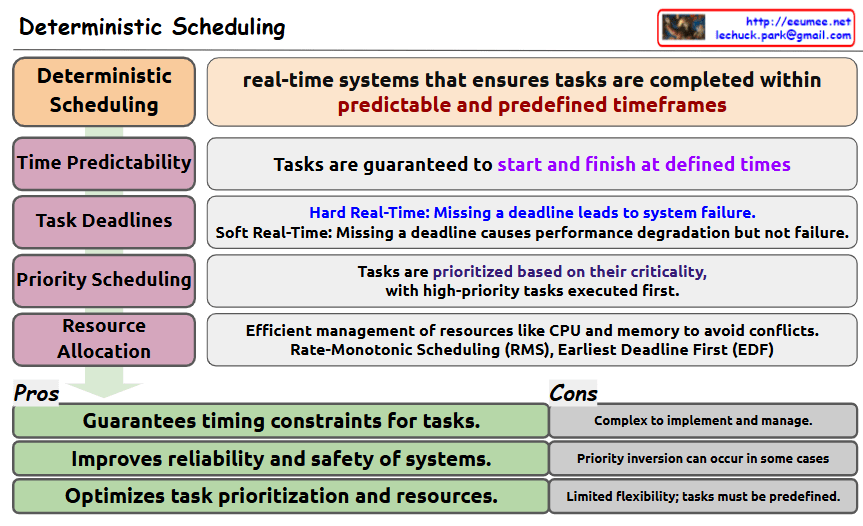
Definition: Deterministic Scheduling is a real-time systems approach that ensures tasks are completed within predictable and predefined timeframes.
Key Components:
- Time Predictability
- Tasks are guaranteed to start and finish at defined times
- Task Deadlines
- Hard Real-Time: Missing a deadline leads to system failure
- Soft Real-Time: Missing a deadline causes performance degradation but not failure
- Priority Scheduling
- Tasks are prioritized based on their criticality
- High-priority tasks are executed first
- Resource Allocation
- Efficient management of resources like CPU and memory to avoid conflicts
- Uses Rate-Monotonic Scheduling (RMS) and Earliest Deadline First (EDF)
Advantages (Pros):
- Guarantees timing constraints for tasks
- Improves reliability and safety of systems
- Optimizes task prioritization and resources
Disadvantages (Cons):
- Complex to implement and manage
- Priority inversion can occur in some cases
- Limited flexibility; tasks must be predefined
The system is particularly important in real-time applications where timing and predictability are crucial for system operation. It provides a structured approach to managing tasks while ensuring they meet their specified time constraints and resource requirements.