From Claude with some prompting
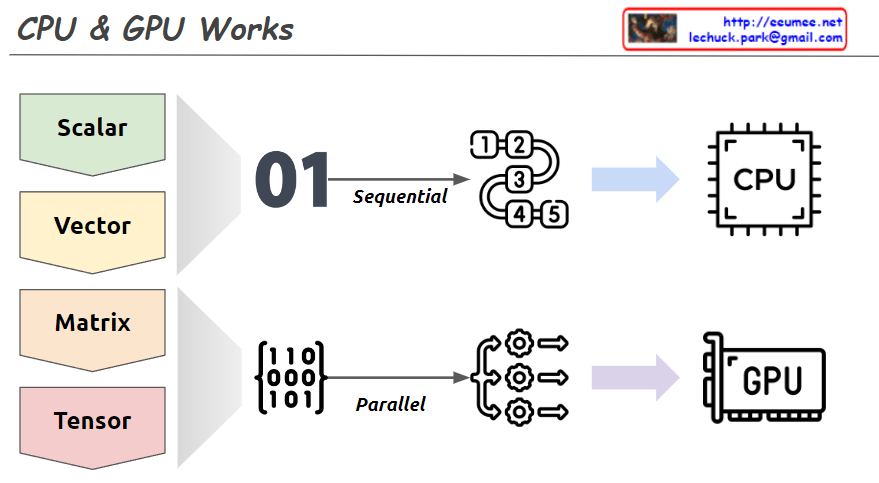
This image explains the working principles of CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) in a visual manner.
- Data Types:
- Scalar: A single value
- Vector: One-dimensional array
- Matrix: Two-dimensional array
- Tensor: Multi-dimensional array
- CPU Work Method:
- Sequential processing, denoted by ’01’
- Tasks are processed in order, as shown by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- Primarily handles scalar data, processing complex tasks sequentially
- GPU Work Method:
- Parallel processing, represented by a matrix
- Icons show multiple tasks being processed simultaneously
- Mainly deals with multi-dimensional data like matrices or tensors, processing many tasks in parallel
The image demonstrates that while CPUs process tasks sequentially, GPUs can handle many tasks simultaneously in parallel. This helps explain which processing unit is more efficient based on the complexity and volume of data. Complex and large-scale data (matrices, tensors) are better suited for GPUs, while simple, sequential tasks are more appropriate for CPUs.

