With a Claude’s help
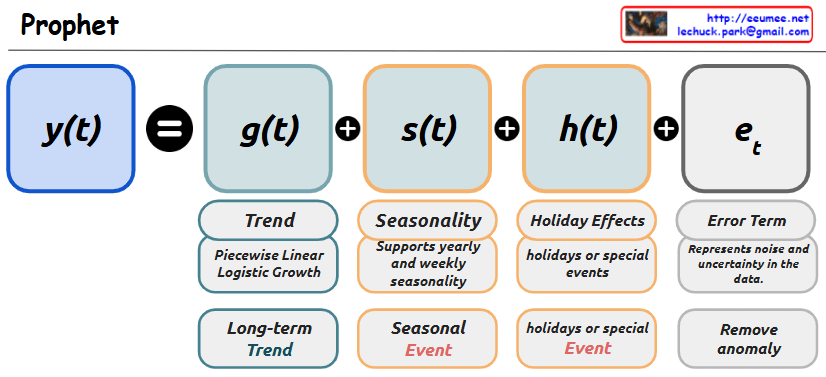
The image appears to be a diagram or concept map that explains the components of the Prophet forecasting model, which is a popular time series forecasting library in Python. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
The diagram also shows different types of trend, seasonality, and holiday effects that the Prophet model can handle.
The main function is y(t), which represents the time series data that needs to be forecasted.
y(t) is composed of four additive components:
g(t): The trend component, which represents the long-term linear or piecewise linear growth trend in the data.
s(t): The seasonality component, which captures yearly and weekly seasonality patterns in the data.
h(t): The holiday effects component, which accounts for the impact of holidays or special events on the data.
e: The error term, which represents noise and uncertainty in the data.

