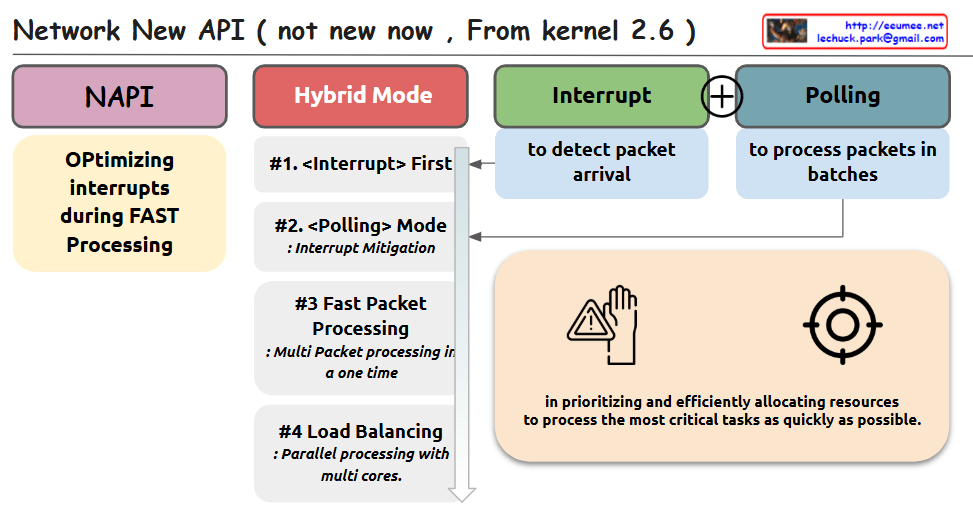
This image shows a diagram of the Network New API (NAPI) introduced in Linux kernel 2.6. The diagram outlines the key components and concepts of NAPI with the following elements:
The diagram is organized into several sections:
- NAPI – The main concept is highlighted in a purple box
- Hybrid Mode – In a red box, showing the combination of interrupt and polling mechanisms
- Interrupt – In a green box, described as “to detect packet arrival”
- Polling – In a blue box, described as “to process packets in batches”
The Hybrid Mode section details four key features:
- <Interrupt> First – For initial packet detection
- <Polling> Mode – For interrupt mitigation
- Fast Packet Processing – For multi-packet processing in one time
- Load Balancing – For parallel processing with multiple cores
On the left, there’s a yellow box explaining “Optimizing interrupts during FAST Processing”
The bottom right contains additional information about prioritizing and efficiently allocating resources to process critical tasks quickly, accompanied by warning/hand and target icons.
The diagram illustrates how NAPI combines interrupt-driven and polling mechanisms to efficiently handle network packet processing in Linux.
With Claude